Hépato-Gastro & Oncologie Digestive
MENUGastrointestinal side effects of immunotherapy Volume 28, issue 8, Octobre 2021
- Key words: anti-TNF, colitis, corticosteroid therapy, immunotherapy
- DOI : 10.1684/hpg.2021.2221
- Page(s) : 951-8
- Published in: 2021
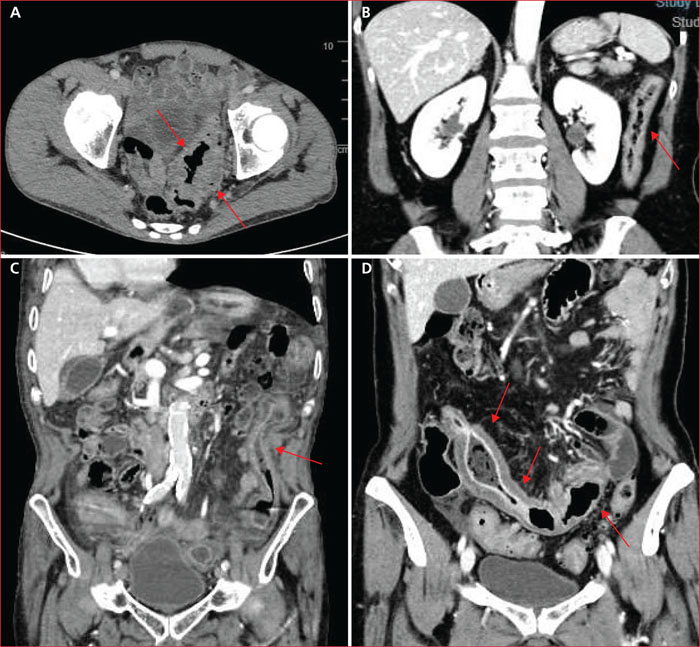
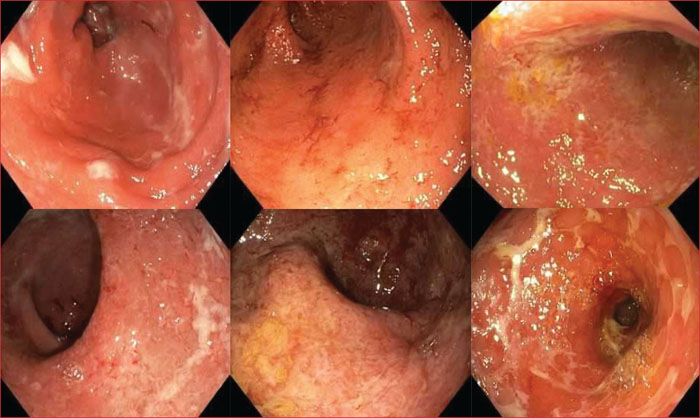
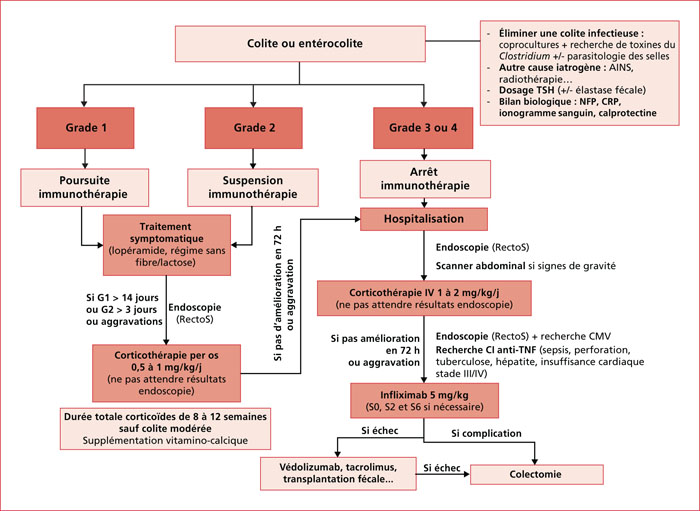
With the increasing use of immunotherapy in oncology, clinicians will be faced more and more with immune-related adverse effects. As the digestive toxicities of immunotherapy are among the most frequent, it is important for gastroenterologists to know the clinical presentation, the diagnostic methods and the therapeutic management. The diagnosis of immuno-induced colitis requires to rule out differential diagnoses, in particular infectious ones, and endoscopic evaluation with biopsies in severe and/or refractory cases. In most cases, stopping immunotherapy and starting corticosteroid therapy quickly results in rapid improvement in symptoms. In case of worsening or resistance to corticosteroid therapy, the second-line treatment is infliximab. Anti-TNFα must be early administered to avoid the occurrence of a complication which sometimes requires surgical management. Resumption of immunotherapy is possible after a mild side effect but should be discussed on a case-by-case basis in other situations, ideally during multidisciplinary meetings dedicated to the management of these toxicities.