Hépato-Gastro & Oncologie Digestive
MENUDigestive amyloidosis: From diagnosis to treatment Volume 25, issue 5, Mai 2018
- Key words: amyloidosis, diarrhea, intestinal malabsorption, pseudo intestinal obstruction
- DOI : 10.1684/hpg.2018.1614
- Page(s) : 451-60
- Published in: 2018
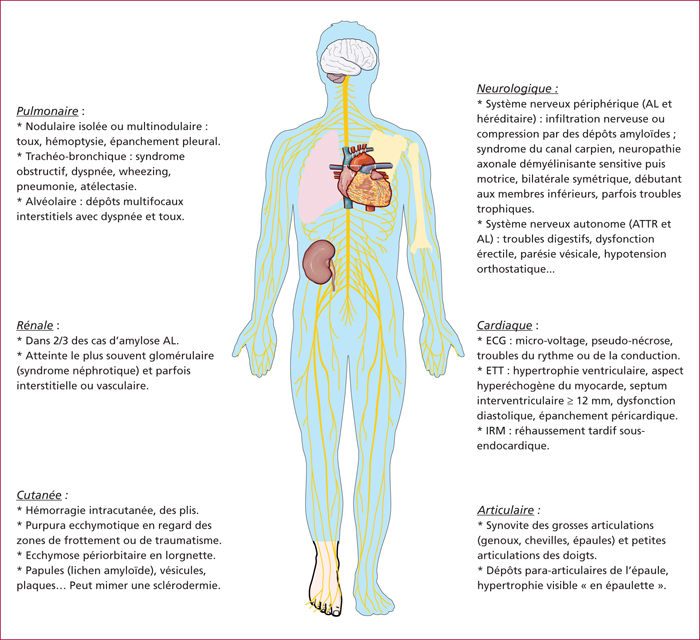
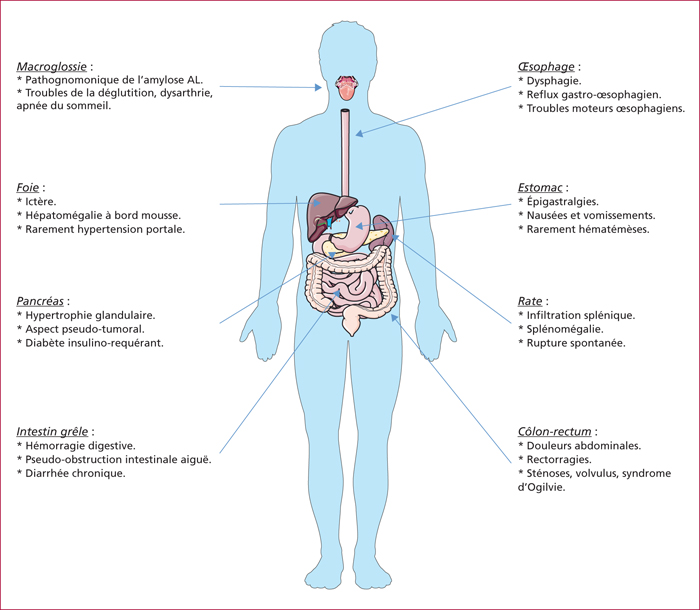
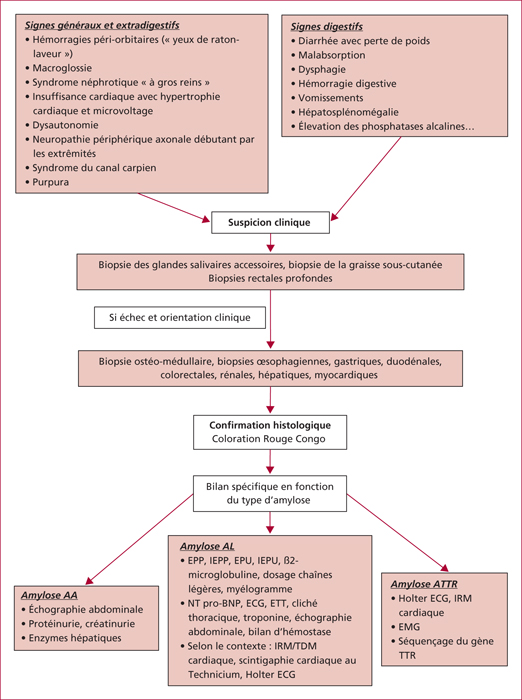
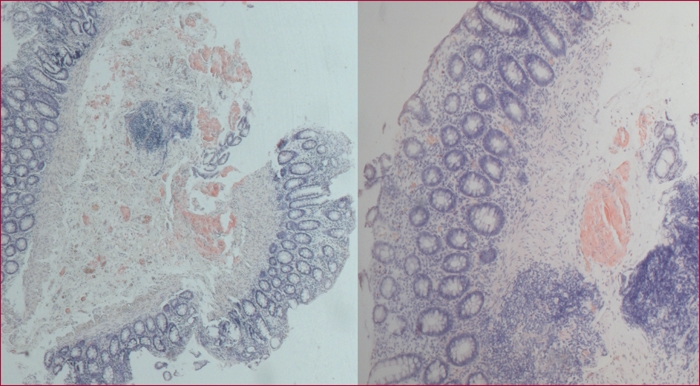
Amyloidosis is a rare entity featured by a misfolding of protein pathology, defined by an extracellular amyloid deposition in tissues. Each amyloidosis is distinguished by the type of fibrillar protein involved, and each form has its own clinical features and treatment. The diagnosis is based on histology after Red Congo staining, polarized light shows a green birefringence which is pathognomonic. Gastrointestinal and hepatic involvement is frequent, and may be the first symptoms of the disease. Thus it is important to think about amyloidosis in case of unexplained clinical presentation as motility disorder, chronic diarrhea, unexplained intestinal malabsorption, intestinal pseudo-obstruction, or hepatosplenomegaly to look for extradigestive impairment and to start a treatment as quickly as possible. Nevertheless, the prognosis remains poor, and mainly depends on cardiac and renal failures.
![]() This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License