Environnement, Risques & Santé
MENUWind turbines and health: a review with suggested recommendations Volume 18, issue 2, March-April 2019
Figures
Institut de santé globale, Campus Biotech,
9, chemin des Mines
1202 Genève
Suisse
Faculté des sciences de la société
40, boulevard du Pont-d’Arve
1205 Genève
Suisse
- Key words: renewable energy, wind, quality of life, environmental policy, health, noise
- DOI : 10.1684/ers.2019.1281
- Page(s) : 149-59
- Published in: 2019
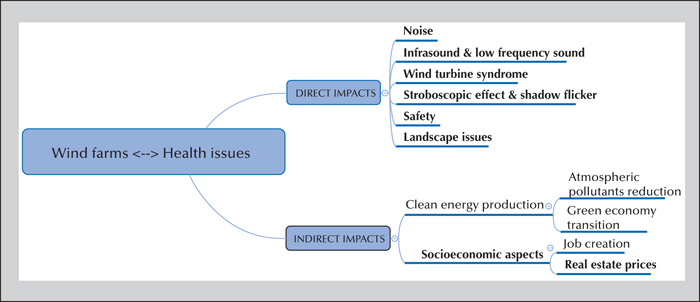
Wind energy has considerable potential worldwide; however, several health concerns are associated with its development. Based on a structured search of the international scientific literature, this review investigates the main health concerns, grouped into the following categories: noise, infrasound and low-frequency sounds, wind turbine syndrome, stroboscopic effect and shadow flicker, safety, landscape impacts, and real estate prices. There is a geographical mismatch between the globally positive aspects of wind farm development and the possible health effects on the neighbourhood, which are the focus of this review. Health complaints are often difficult to link firmly to the activity of adjacent wind farms, with the exception of annoyance caused by noise pollution. Part of the negative health effects reported by local populations may be influenced by the so-called nocebo effect. However, discomfort and suffering should always be addressed and taken seriously into account by decision-makers and public health officials. The distribution of economic and health-related advantages and inconveniences should be perceived as being fair. This article concludes with a 9-point list of recommendations for the development of wind power in a context favourable to health.
![]() This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License