Environnement, Risques & Santé
MENUEndocrine disruptors and the thyroid gland Volume 16, issue 6, November-December 2017
Authors
Université de Lorraine
Faculté de pharmacie de Nancy
EA 3452 CITHEFOR18, rue
Lionnois
54000 Nancy
France
Faculté de pharmacie de Nancy
EA 3452 CITHEFOR18, rue
Lionnois
54000 Nancy
France
* Tirés à part
- Key words: thyroid hormones, thiocyanate, flavonoid, drugs interactions, bisphenol A
- DOI : 10.1684/ers.2017.1093
- Page(s) : 583-90
- Published in: 2017
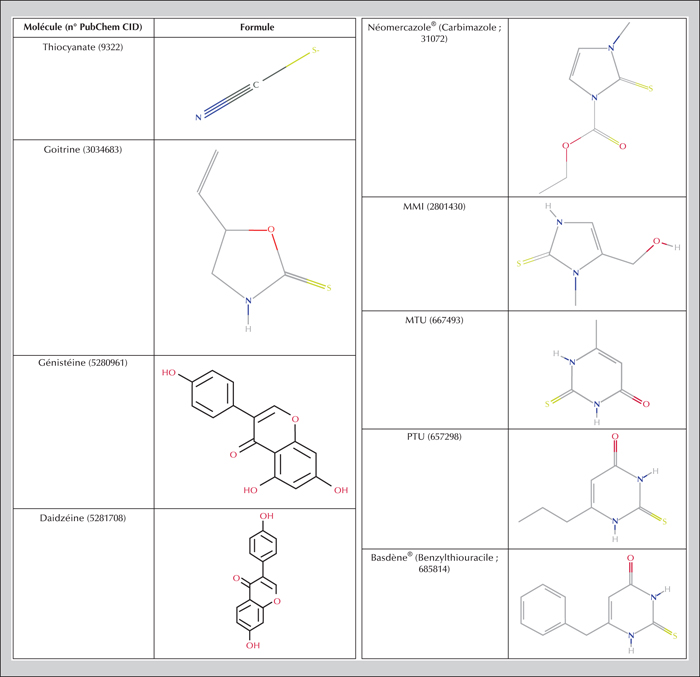
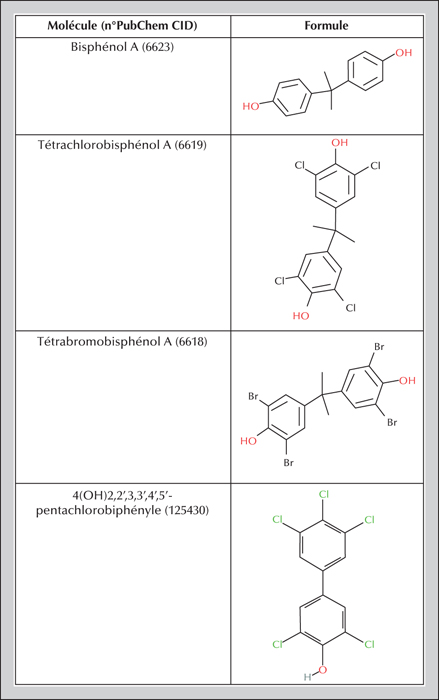
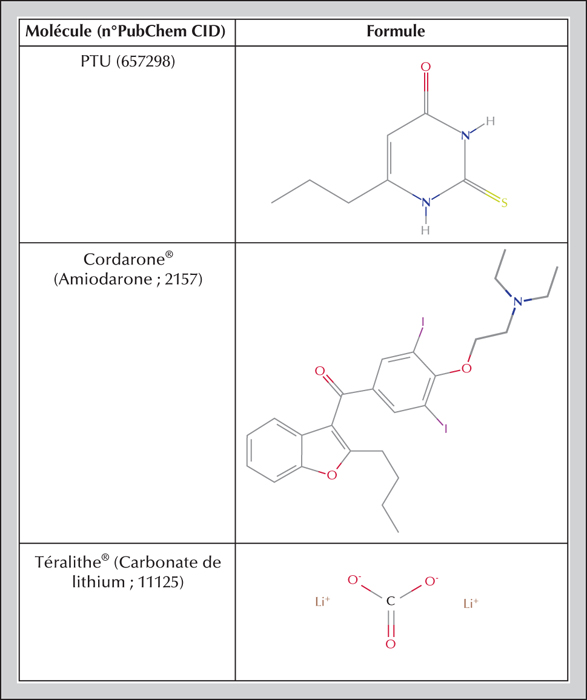
Today there are many synthetic molecules of human origin in our environment, some recent, others much older. This review of data from the biomedical literature on thyroid endocrine disruptors seeks to determine which endocrine disruptors, natural or synthetic, affect the thyroid and how they disturb its function. Few studies on this topic use isolated organs to determine the effects of these compounds. Moreover, as assays consider one or two molecules, it is difficult to dissociate endocrine disruptor effects on the thyroid from effects on the whole organism. We therefore cannot conclude whether endocrine disruptors are the sole cause of thyroid disease.