Néphrologie & Thérapeutique
MENUPregnancy after kidney transplantation: Ibn Sina Rabat University hospital experience Volume 19, issue 2, April 2023
- Key words: pregnancy, ESKD, immunosuppression, kidney transplantation
- DOI : 10.1684/ndt.2023.2
- Page(s) : 109-20
- Published in: 2023
Introduction
Kidney transplantation (KT) restores the fertility of women with end-stage kidney disease (ESKD), thus offering them the possibility of having children. However, pregnancy after kidney transplantation is associated with high maternal-fetal morbidity. The purpose of this work is to report the experience of our service in pregnancies in kidney transplant recipients.
Materials and methods
We retrospectively studied the records of transplant recipients who had one or more pregnancies after KT. We analyzed clinical (blood pressure, weight gain, oedema, duration of pregnancy, obstetric complication) and biological (creatinine, urinary albumin excretion) parameters.
Results
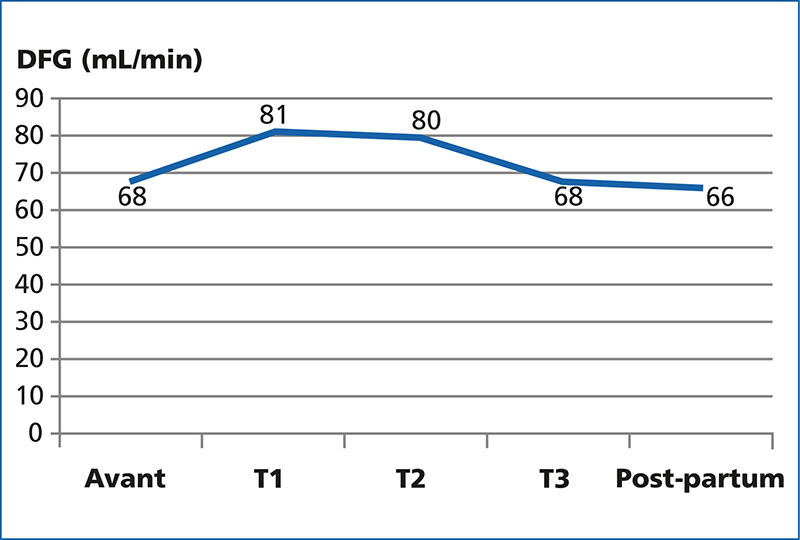
Between 1998 and 2020, twenty-one pregnancies occurred in 12 transplant recipients. The average age of patients at the time of conception was 29 ± 5 years with a delay between KT and pregnancy of 43 ± 29 months. Seven pregnancies began with arterial hypertension (HTA) controlled under treatment, proteinuria before conception was negative in all pregnancies and renal function was normal with an average creatinine level of 10.1 ± 1,27 mg/L. Prior to pregnancy, immunosuppression regimens were based on anticalcineurin (n = 21) combined either with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) (n = 10) or azathioprine (n = 8) or alone (n = 3). Immunosuppression regimens were all associated with corticosteroid therapy. Three months before conception, MMF was relayed by azathioprine in seven pregnancies, on the other hand three other unplanned pregnancies, started under MMF. During pregnancy, the appearance of proteinuria greater than 0,5 g/24 h was noted in three pregnancies in the third trimester. Pregnancy hypertension was found in three pregnancies, one of which progressed to pre-eclampsia. As for renal function, it remained stable with an average creatinine level of 10,3 mg/l in the 3rd trimester. Two cases of acute pyelonephritis were noted. No episode of acute rejection was noted during and 3 months after pregnancy. The delivery was performed by caesarean section in 44.4 %, after an average term of 37 week of amenorrhea ± 2.04 with three cases of prematurity. The average birth weight was 3 110 g ± 450 g. There was one case of spontaneous abortion and two cases of fetal death in utero. After post-partum, renal function remained stable in five patients. In six cases, there was impaired renal function either by acute rejection or secondary to chronic allograft nephropathy.
Conclusion
In our department, a quarter of transplant recipients were able to carry a pregnancy with a rate of 89 % of successful pregnancies. Pregnancy after KT requires special planning and monitoring. A multidisciplinary collaboration between transplant nephrologist, gynecologist and pediatrician is necessary by referring to the recommendations.