Journal de Pharmacie Clinique
MENUEvaluation of antibiotic prophylaxis practices in scheduled surgery Volume 38, issue 2, Juin 2019
- Key words: antibiotic prophylaxis, scheduled surgery, practices evaluation
- DOI : 10.1684/jpc.2019.0411
- Page(s) : 81-9
- Published in: 2019
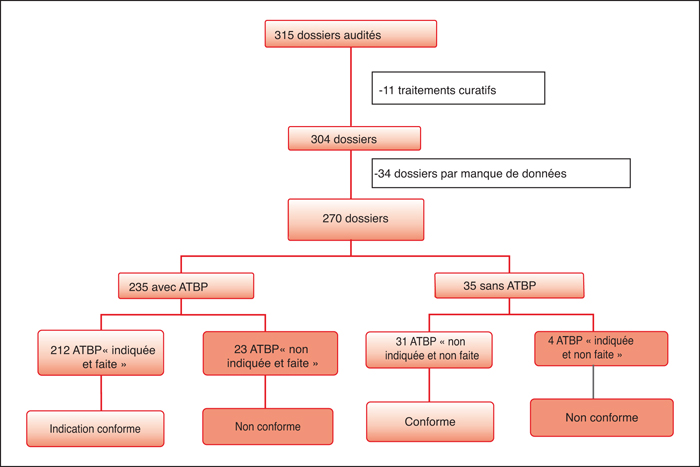
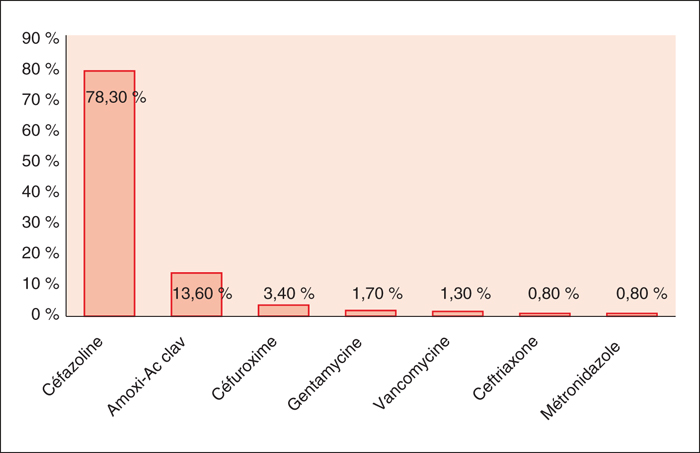
Antibiotic prophylaxis (ATBP) is one of the specific measures for the prevention of surgical site infections, whose impact has been quantified in surgery. Material and methods: It is a retrospective multidisciplinary and perprotocol study, performed in the operating room and surgical departments for 315 patients operated for an elective surgery. Data were collected during a six-week period, from June 5 to July 17, 2017. Compliance was assessed by comparing the guidelinesof the French society of anesthesia and intensive care 2017. Results: Among the 270 cases included, 235 cases involve ATBP administration. The overall compliance rate was 53.3%. The compliance with each of the 6 major criteria was 90% for the indication; 57.1% for the administration schedule; 97.6% for repeating the administration; 87.2% for the choice of antibiotic; 91% for the dose of the first administration and 81.6% for the duration of ATBP. The overall compliance was variable depending on the department; less compliance was reported in the urological surgery. Conclusion:A global strategy including organization, education and restriction, could lead to a real improvement in the rate of compliance with ATBP practices. Successive audits should be carried out regularly in order to evaluate the impact of the undertaken actions.
![]() This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License