Hépato-Gastro & Oncologie Digestive
MENUPancreatico-biliary maljunctions Volume 22, issue 5, Mai 2015
service de chirurgie digestive,
20 rue Leblanc,
75015 Paris,
France ;
Université Paris 5,
France
- Key words: pancreaticobiliary maljunctions, bile duct cyst, long common channel, biliary amylase level, biliary cancer
- DOI : 10.1684/hpg.2015.1155
- Page(s) : 370-6
- Published in: 2015
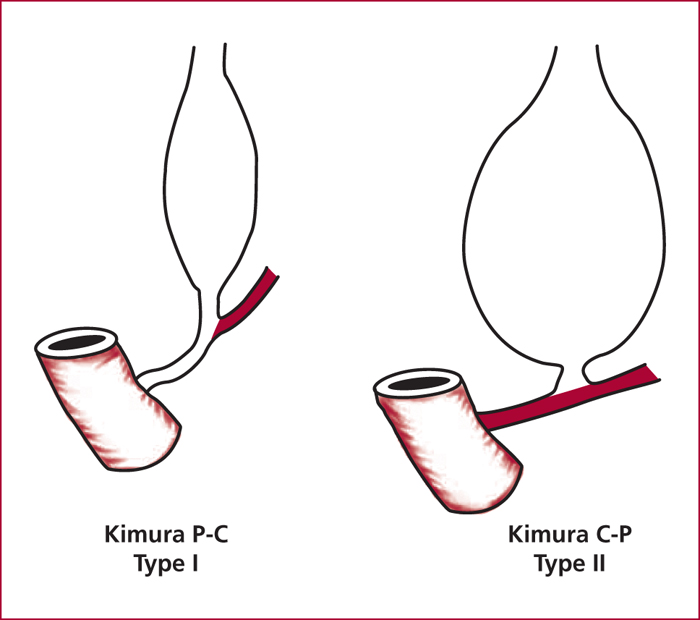
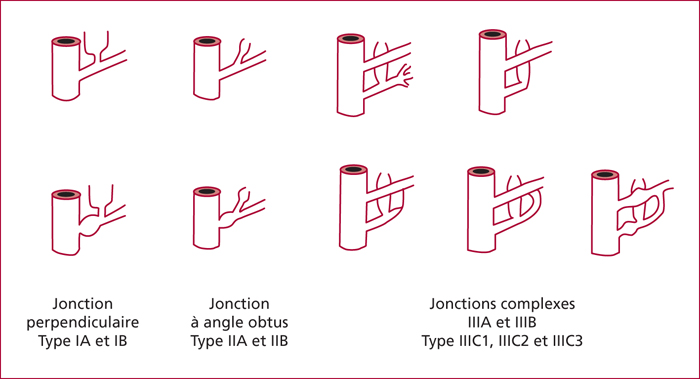
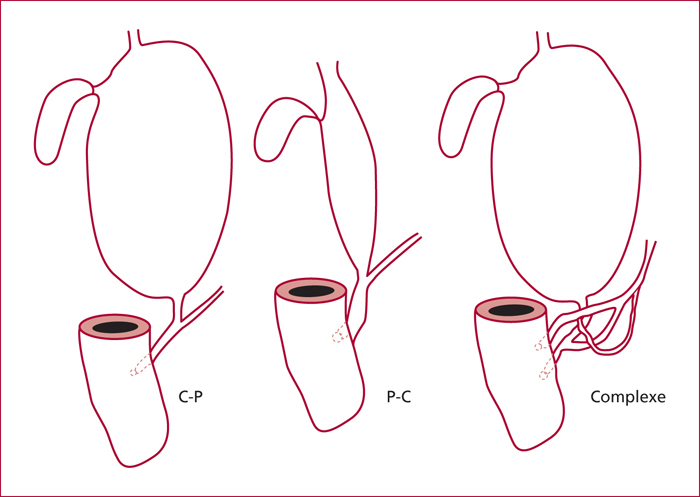
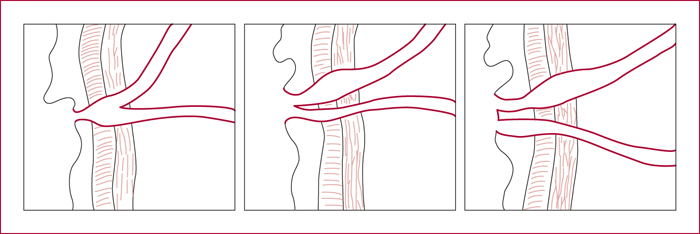
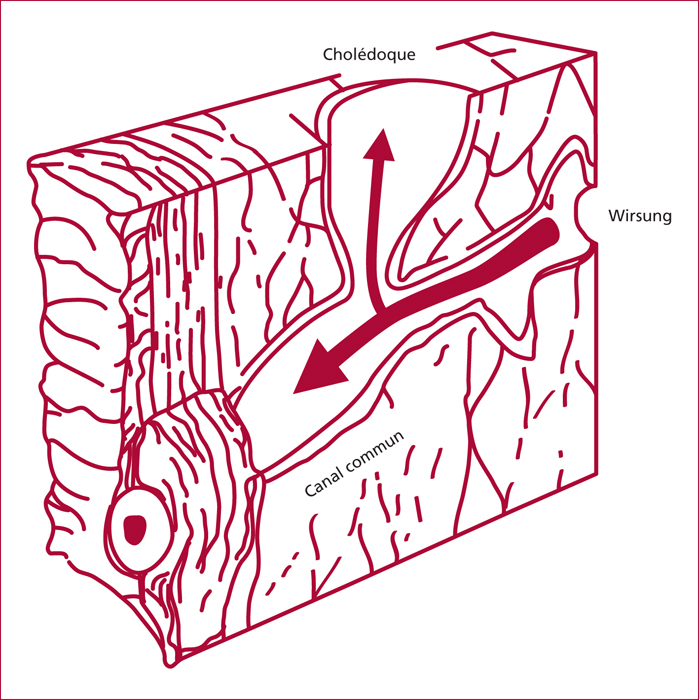
Pancreaticobiliary maljunctions (PBM) are congenital anomalies of the junction between pancreatic and bile ducts that are characterized by an abnormal junction between pancreatic and bile ducts. There are often associated with bile duct cyst (BDC). BDC are congenital anomalies of the biliary tree that are characterized by cystic dilatation of the extra- and/or intrahepatic bile ducts. PBM induce pancreatic juice reflux into the biliary tract that is supposed to induce BDC and development of biliary cancer. They can be defined by morphologic criteria and, among them, a long common channel (>10 mm) is the most important. The incidence of biliary cancer is 17%, it increases with age and after cyst enterostomy. When PBM is associated with BDC, the standard treatment is complete resection of BDC. In isolated PBM, preventive cholecystectomy is recommended.