Hépato-Gastro & Oncologie Digestive
MENUWhat you need to know about gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease Volume 27, issue 10, Décembre 2020
- Key words: Graft versus host disease, allogeneic hematopoietic stem cells transplantation, intestinal barrier, rectosigmoidoscopy, corticosteroids
- DOI : 10.1684/hpg.2020.2086
- Page(s) : 1020-9
- Published in: 2020
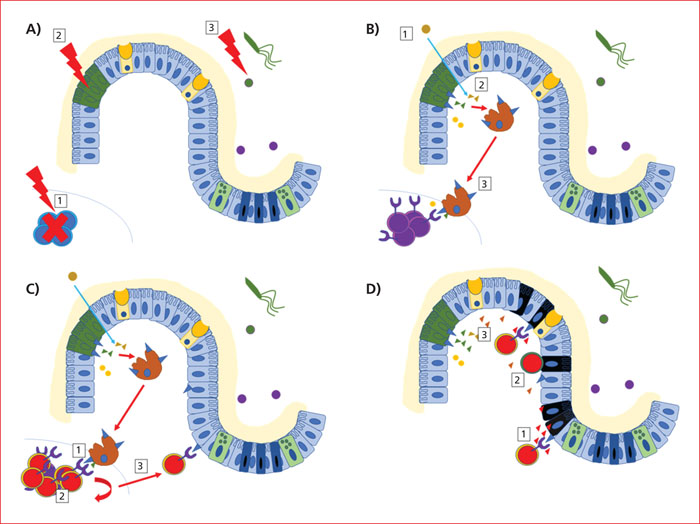
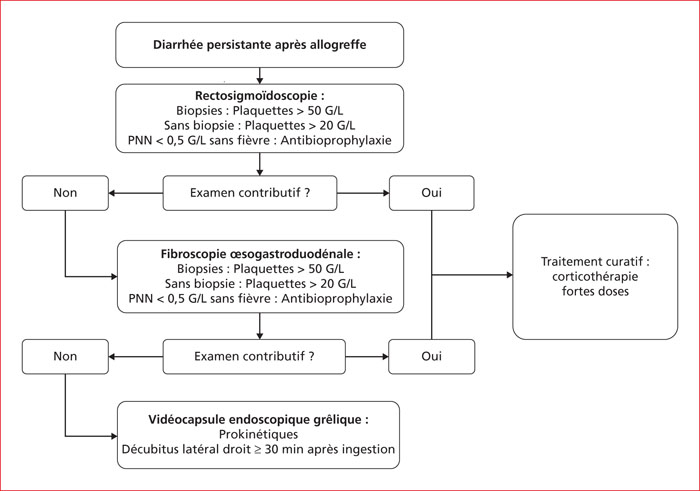
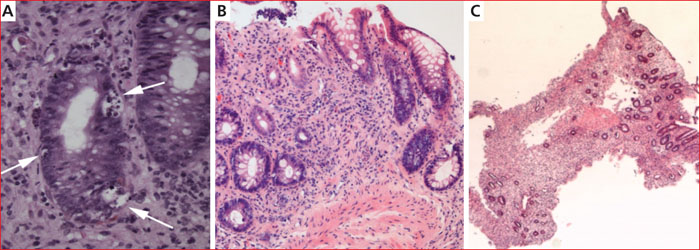
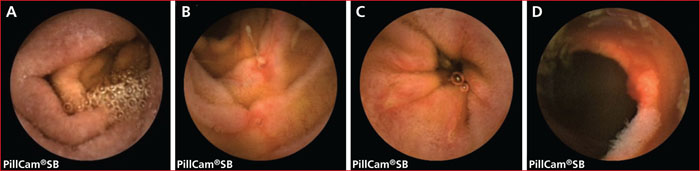
Gastrointestinal acute Graft Versus Host Disease (GI-GVHD) is a complication of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cells transplantation, that usually occurs during the first 100 days after transplantation. Diarrhea is the main symptom, sometimes associated with abdominal pain, weight loss and asthenia. Classically, main risk factors are a patient-unrelated donor and HLA-incompatibility. Pathophysiology of GVHD outbreak requires 3 steps, in which digestive mucosa and microbiota play a pivotal role: first the activation of recipient antigen presenting cells, then activation and migration of donor T lymphocytes and finally destruction of host tissues. GI-GVHD diagnosis is based on a range of arguments, above all clinical, and is a diagnosis of elimination. However, digestive explorations are an important diagnostic aid. In case of diarrhea, a rectosigmoidoscopy with multiple biopsies should first be performed, although upper digestive endoscopy with duodenal biopsies has also an acceptable diagnostic accuracy. However, endoscopic and histological signs, like clinical symptoms, are non-specific. Main differential diagnoses are drug-induced lesions (conditioning chemotherapy, mycophenolate mofetil…), infectious diseases (CMV and Clostridioides difficile colitis…) and neutrophilic colitis. Prevention relies on immunosuppressive treatments. First line curative treatment relies on high doses of corticosteroids. If corticosteroids fail, second-line treatments can be proposed, such as anti-TNF, anti-integrins, transplantation of fecal microbiota.