Epileptic Disorders
MENUVideo‐EEG evidence of lateralized clinical features in primary generalized epilepsy with tonic‐clonic seizures Volume 5, issue 3, September 2003
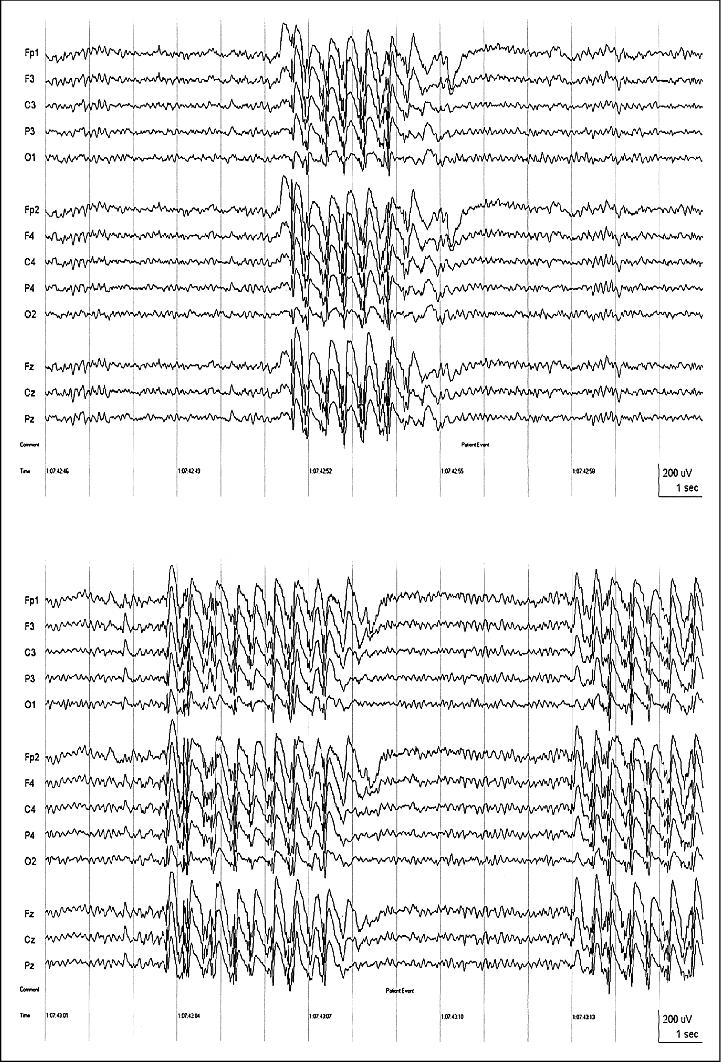
Figure 1. Interictal EEG of patient J.L. Sequential pages of the EEG showing generalized polyspike-and-wave activity associated with myoclonic jerks (note Patient Event marker) just prior to the ictal event in Figure 2; referential longitudinal montage, t9-t10 averaged reference (all figures); 70 Hz high frequency filter (HFF), time constant (TC) = 0.3 sec.
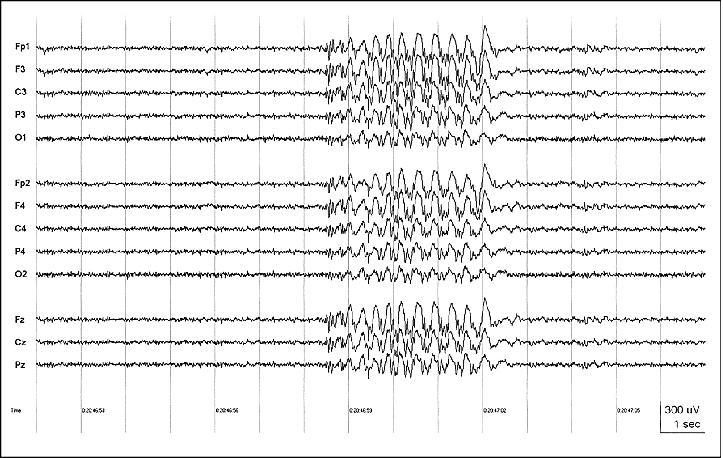
Figure 2. Patient J.L. Ictal EEG onset of the seizure in Videosequence 1; clinical seizure onset at*; 15 Hz HFF to highlight ictal pattern (obscured by muscle artifact with 70 Hz HFF), TC = 0.3 sec.
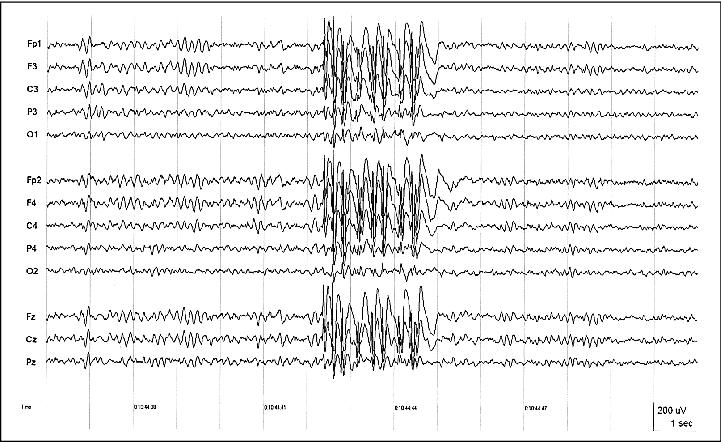
Figure 3. Interictal EEG of patient S.W. showing a typical generalized polyspike-and-wave discharge; 70 Hz HFF, TC = 0.3 sec.
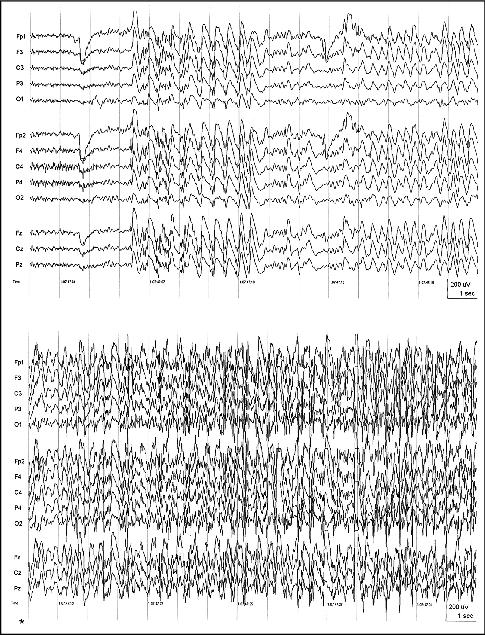
Figure 4. Patient S.W. Ictal EEG onset of the seizure in Videosequence 2; clinical motor seizure onset at*; 15 Hz HFF, TC = 0.3 sec.
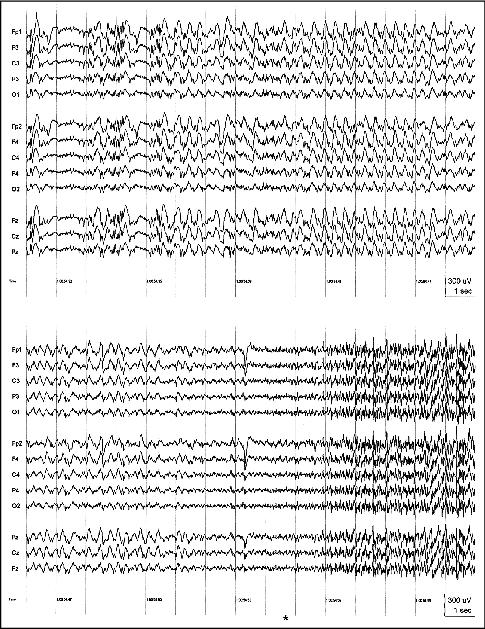
Figure 5. Interictal EEG of patient M.M. showing a typical generalized spike-, and polyspike-and-wave discharge; 70 Hz HFF, TC = 0.3 sec.
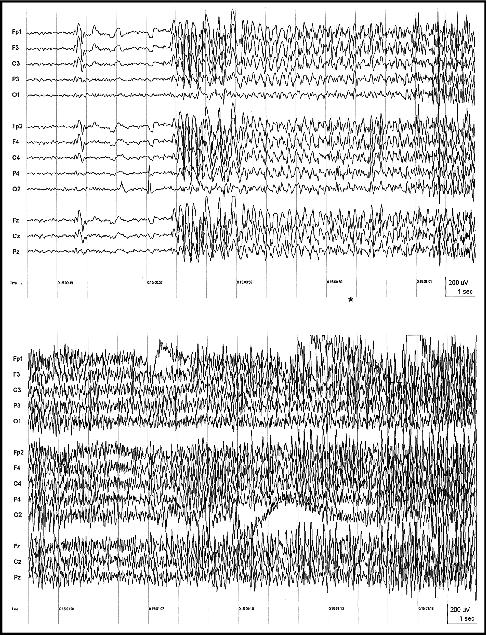
Figure 6. Patient M.M. Ictal EEG onset of the seizure in Videosequence 3; clinical seizure onset at *; 15 Hz HFF, TC = 0.3 sec.

