Epileptic Disorders
MENUSturge-Weber syndrome: a favourable surgical outcome in a case with contralateral seizure onset and myoclonic-astatic seizures Volume 13, issue 1, Mars 2011
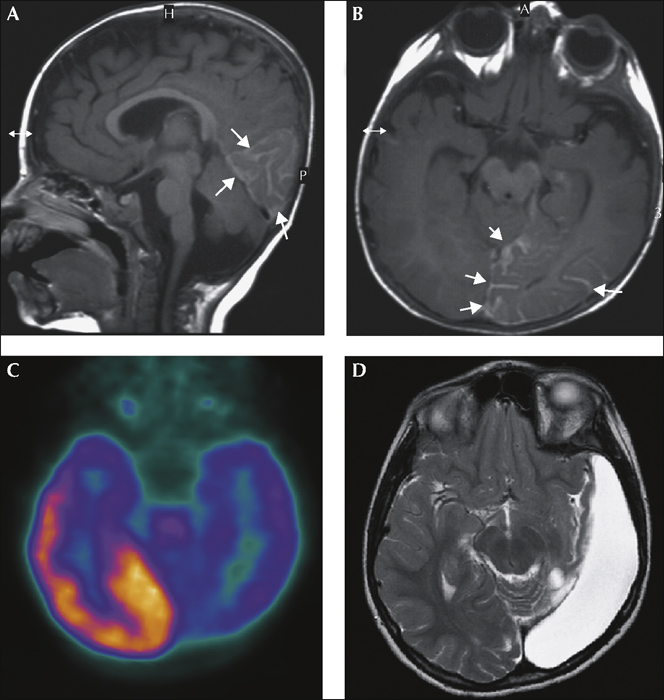
Figure 2 Structural and functional imaging. Sagittal (A) and axial (B) T1-weighted MR images with gadolinium enhancement of leptomeningeal angiomatosis in the left occipitotemporal area (white arrows) and atrophy of adjacent cortex. C) FDG-PET axial scan showing hypometabolism extending beyond the area of angiomatosis. D) Postoperative MRI, axial T2-weighted image. (Department of Radiological Techniques, Motol Hospital, Prague and PET Center, Na Homolce Hospital, Prague)
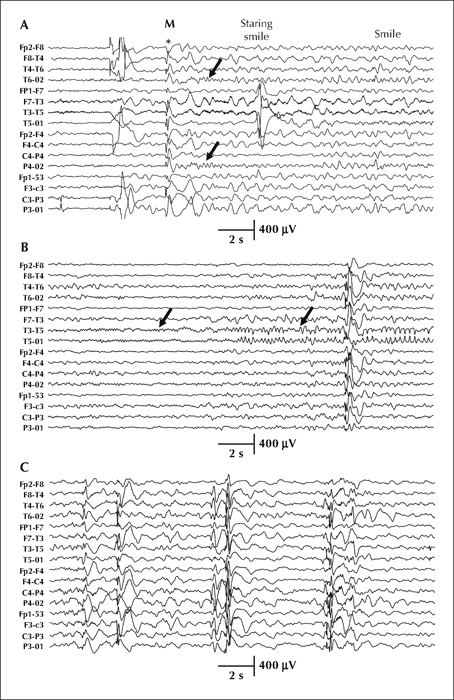
Figure 1 Seizures and interictal activity. Bipolar montage. A) The seizure started with generalised (bilateral synchronous) high-amplitude discharge (*) accompanied by myoclonia of the upper extremities (M) and was followed by rhythmic theta (5.5âHz) over the right occipital region (black arrows). This rhythm was associated with, and followed by, a prolonged episode of staring, eye deviation to the left and inappropriate smiling. The entire seizure evolution is presented in supplementary figure 1. B) Ictal recording of rare seizure onset from the left occipital region. Low-amplitude beta activity evolving later into high-amplitude rhythmic alpha (arrows). This electrographic seizure had no correlate with behaviour. C) Interictal EEG with bilateral synchronous discharges of spike-and-wave complexes or polyspike-and-wave complexes.

