Epileptic Disorders
MENUDeep brain stimulation of the anterior nucleus of the thalamus in a patient with super-refractory convulsive status epilepticus Volume 21, issue 4, August 2019
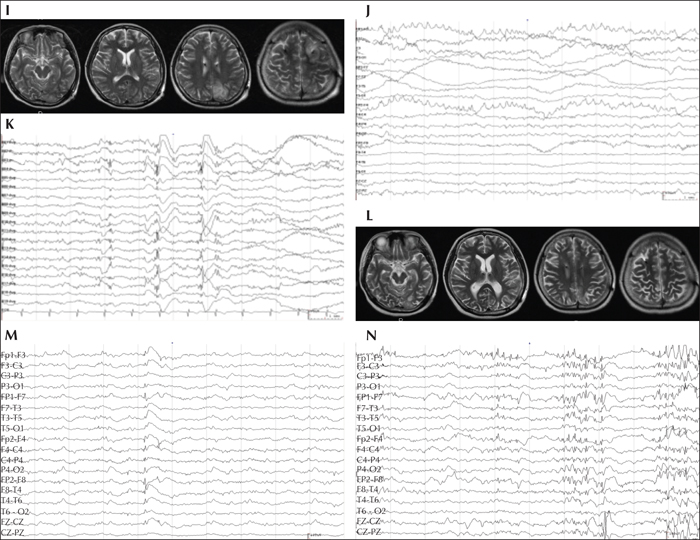
Figure 1
Preoperative (A-H) neuroimaging and EEG findings of the patient. Before the SE, the patient's MRI did not reveal an obvious abnormality in the brain (A). After the SE, ictal positron emission tomography (PET) showed multiple hypermetabolic foci, and the brain MRI showed multiple abnormal signals during the early stage (B, C). A preoperative scalp EEG showed generalized epileptiform discharges with maximal amplitude over bilateral frontal lobes during the interictal period and generalized onset within the ictal period. Postoperative (I-N) neuroimaging and EEG findings of the patient. Brain MRI showed multiple abnormal signals during the early stage (I) and diffusive brain atrophy (L) in the late stage. Electrode signals in the ANT and frontal lobes on brain MRI were present after ANT-DBS treatment (I, L). A post-operative interictal scalp EEG showed that the diffusive epileptiform discharges decreased after the stimulator was turned on and increased after the stimulator was turned off.
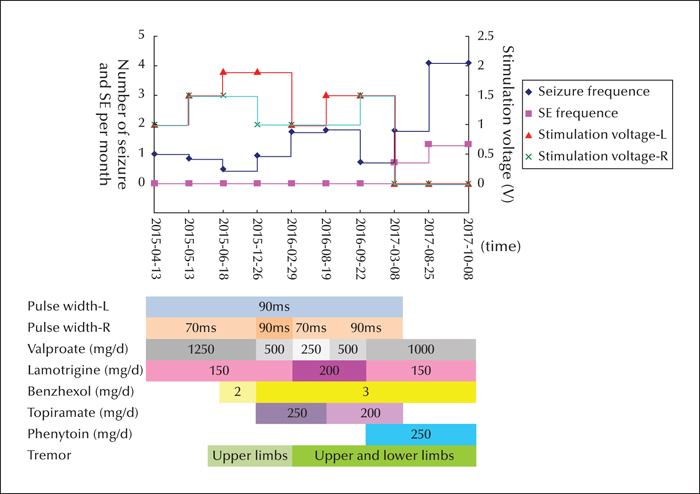
Figure 2
Stimulation voltage and seizure and SE frequency (upper panel) and pulse width, drugs administered, and presence of tremor (lower panel) at different times after ANT-DBS. The SE was controlled after the stimulator was turned on, but recurred after the stimulator was turned off. The patient's tremor did not improve following decreased valproate dosage or stimulation voltage and pulse width (SE: status epilepticus).

