Hépato-Gastro & Oncologie Digestive
MENUVascular liver diseases Volume 25, issue 8, Octobre 2018
- Key words: nodular regenerative hyperplasia, obliterative portal venopathy, portal vein thrombosis, anticoagulation
- DOI : 10.1684/hpg.2018.1665
- Page(s) : 755-63
- Published in: 2018
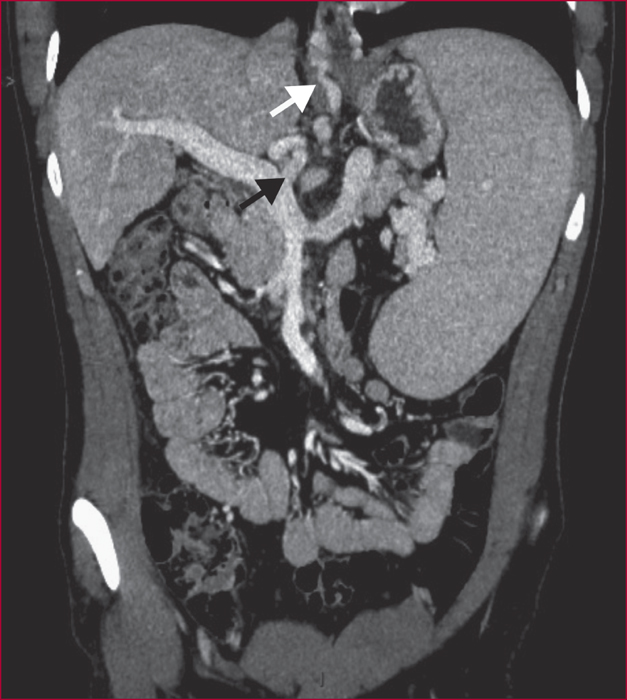
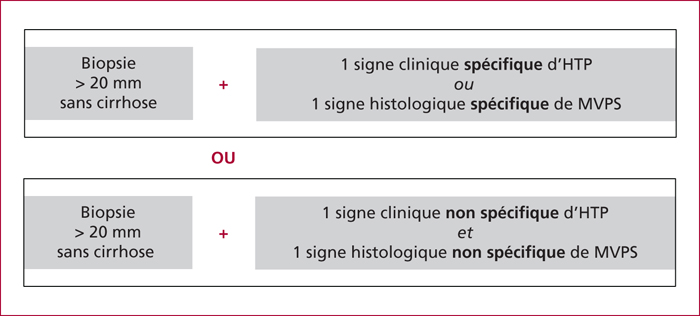
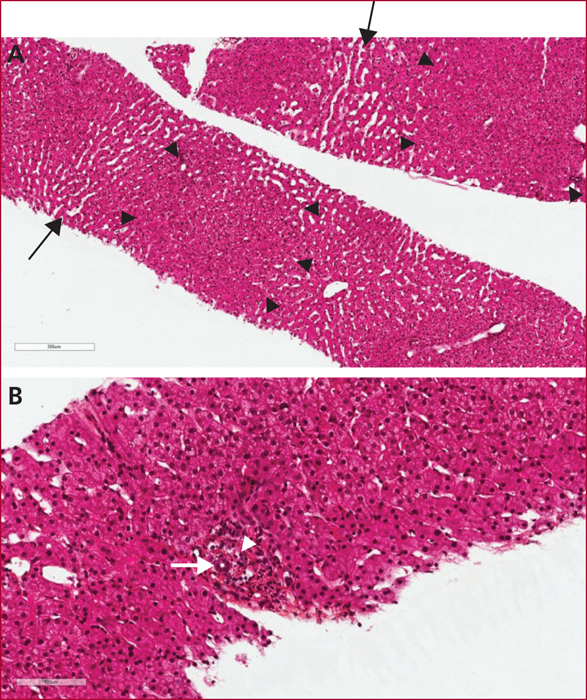
The term “porto-sinusoidal vascular disease” (PSD) encompasses various entities characterized by alterations of the portal venules and/or the sinusoids, called idiopathic portal hypertension, intrahepatic non-cirrhotic portal hypertension, obliterative portal venopathy, or nodular regenerative hyperplasia. Different conditions can be associated with PSD including prothrombotic states, immune-based diseases, HIV infection and antiretroviral treatment, other medications and prothrombotic factors. Liver biopsy is crucial for the diagnosis of PSD. The main complications of PSD are variceal bleeding and portal venous system thrombosis. Therapeutic options currently available for patients with PSD include prophylaxis for variceal bleeding using betablockers and/or endoscopic band ligation and TIPSS (transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt) or liver transplantation for severe cases.
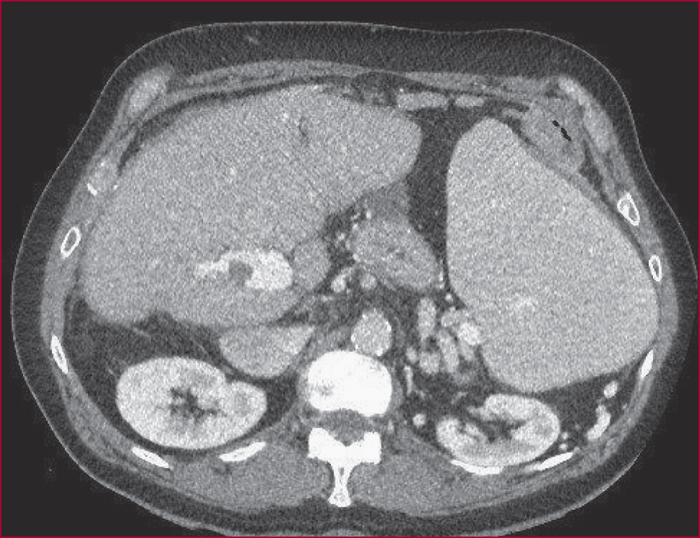
Portal vein thrombosis (PVT) is common in patients with cirrhosis. PVT is partial in a majority of the patients in whom it develops and may spontaneously resolve in some of them. PVT is associated with features of more severe liver disease. Anticoagulation should be considered in patients with superior mesenteric vein thrombosis, and in patients who are potential candidates for liver transplant. The risk of bleeding does not seem to be increased in patients with cirrhosis receiving anticoagulation therapy, when platelet count is above 50 000/mm3.
![]() This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License