Epileptic Disorders
MENUHypothalamic hamartoma and epilepsy in children: illustrative cases of possible evolutions Volume 5, issue 4, December 2003
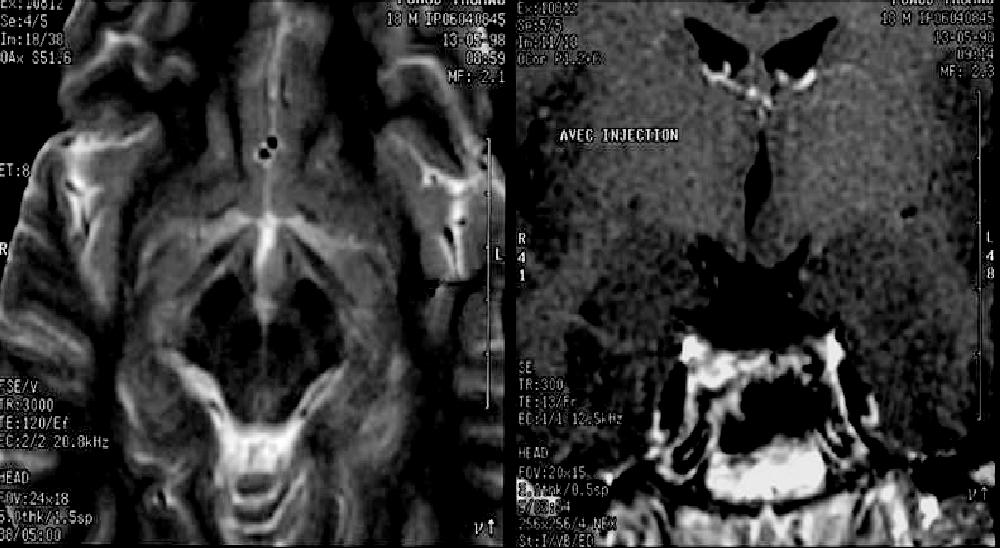
Figure 1. Hypothalamic hamartoma of a relatively small size impinging on the left side of the 3rd ventricle (Patient 1).
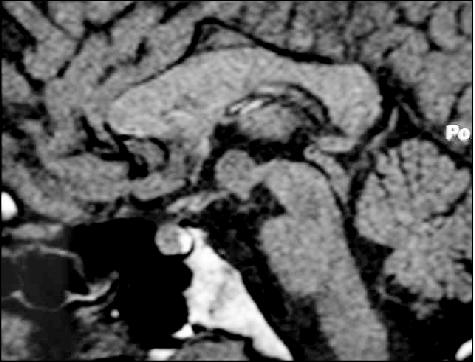
Figure 2. Sagittal view of the HH before radiosurgery (patient 2).
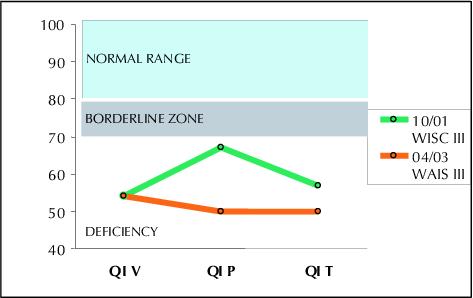
Figure 3. Evolution of verbal and performance IQ in patient 2, evaluated after an 18 months interval. Despite radiosurgery her verbal capacities remained stable while her non verbal performances deteriorated (Courtesy Agathe Laurent, Neuropsychologist, Robert Debré Hospital)
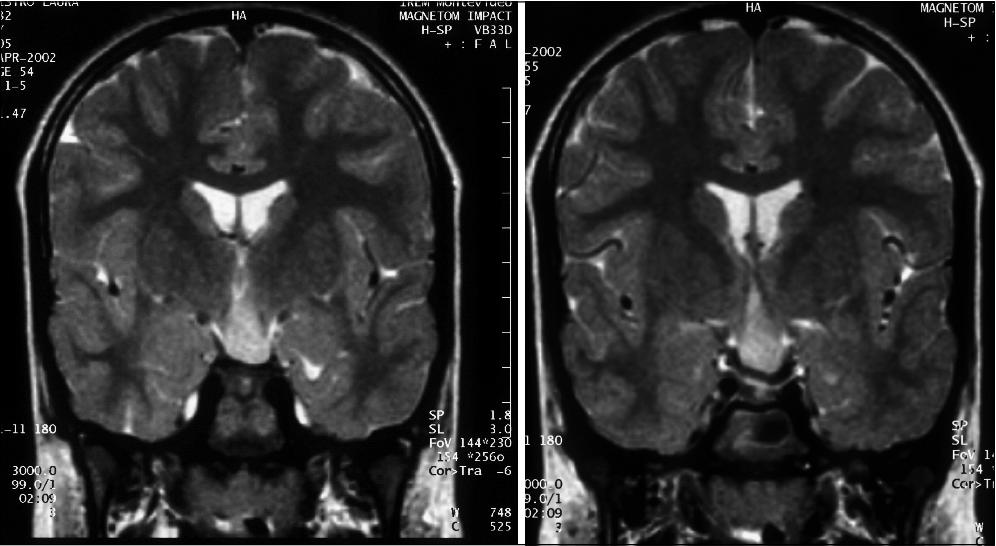
Figure 4. Despite of the size of the HH,
evolution of the epilepsy in patient 4 remains relatively
benign
(Courtesy Drs Ruggia and Diamant, Uruguay).
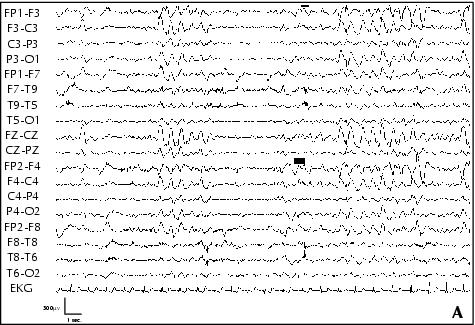
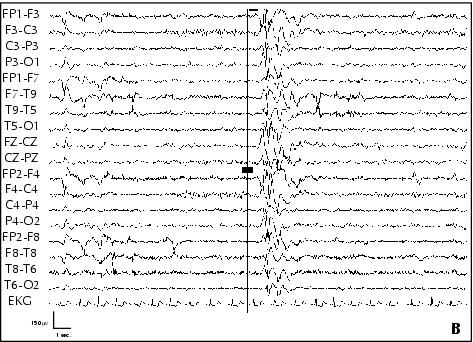
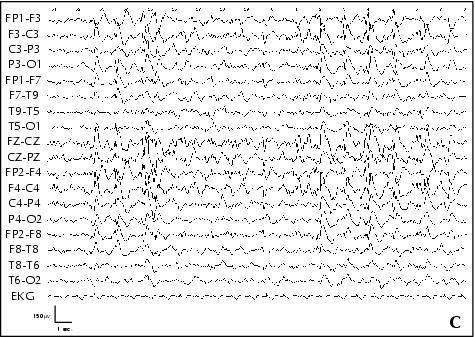
Figure 5. Patient 5. A: EEG performed at age 10, awake, showing bilateral fronto-central asymmetric spike-waves discharges, with a left predominance. B: EEG performed at age 10, awake, showing bilateral polyspike-waves on a normal background activity. C: Sleep EEG performed at age 10, showing bilateral fronto-central spike-waves during Stage 2-3 NREM sleep.
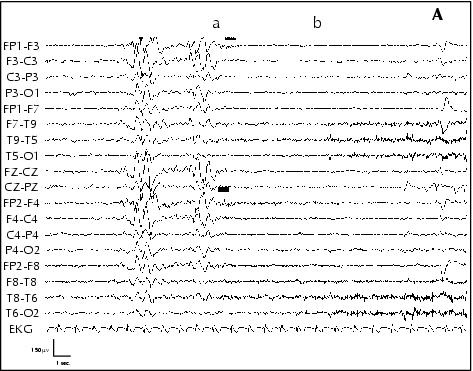
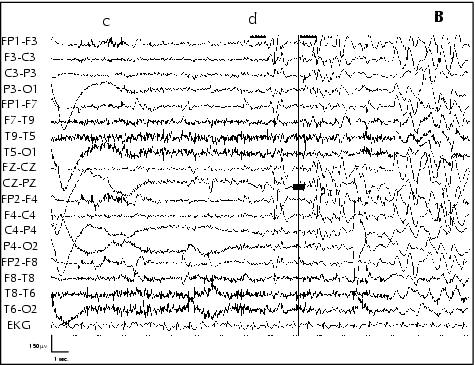
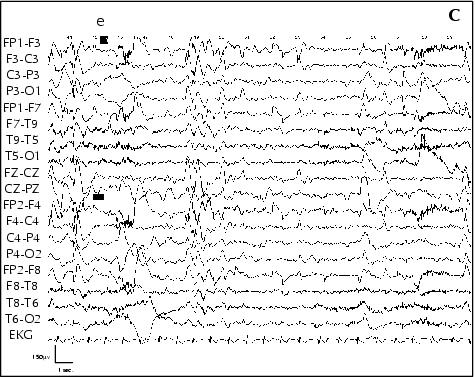
Figure 6. Patient 5. A: Ictal EEG performed awake, at age 10 years: a) gelastic seizure onset with bilateral flattening of EEG activity, b) smiling; B: c) laughing, d) Injection of ECD for SPECT; C: e) end of seizure.
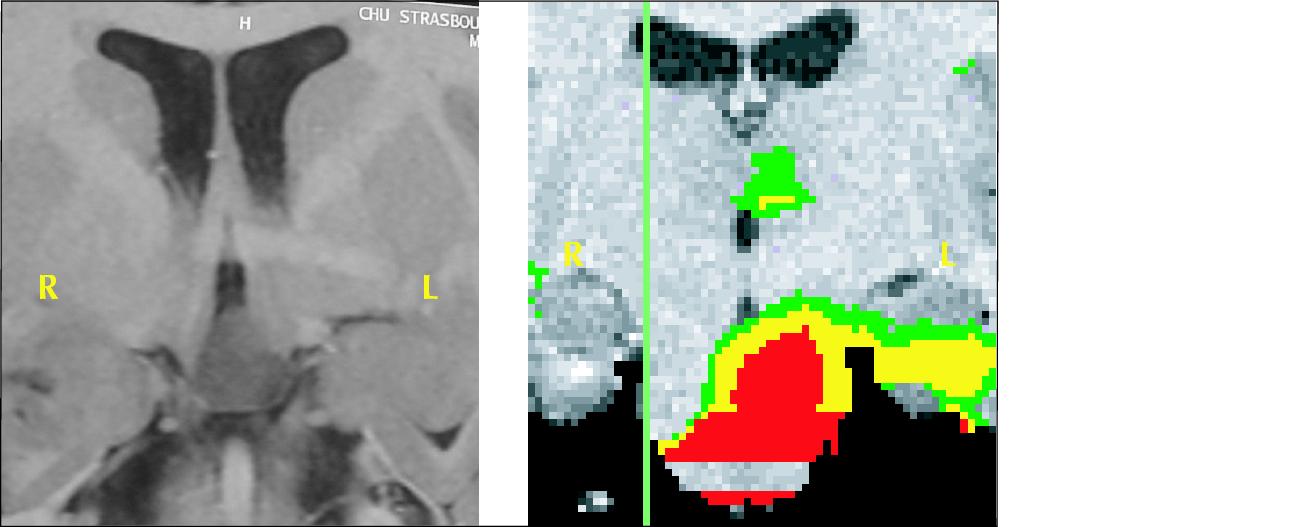
Figure 7. Patient 5. Left, Inversion Recovery MRI Coronal section, hypothalamic hamartoma in the flour of the third ventricule. Right, SISCOM (Substraction Ictal SPECT Coregistered to MRI) showed increased blood flow in the hamartoma and the amygdala.
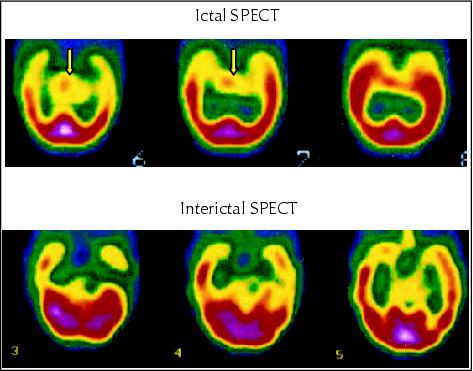
Figure 8. SPECT with ECD, axial section, evidenced focal sub-cortical increase in blood flow at the level of the hypothalamus.

Figure 9. Patient 6. MRI Coronal section, hypothalamic hamartoma on the left wall of the third ventricule, Left, Inversion Recovery, Right, FLAIR.

Figure 10. Patient 6. Interictal SPECT showing left temporal pole decrease of blood flow.
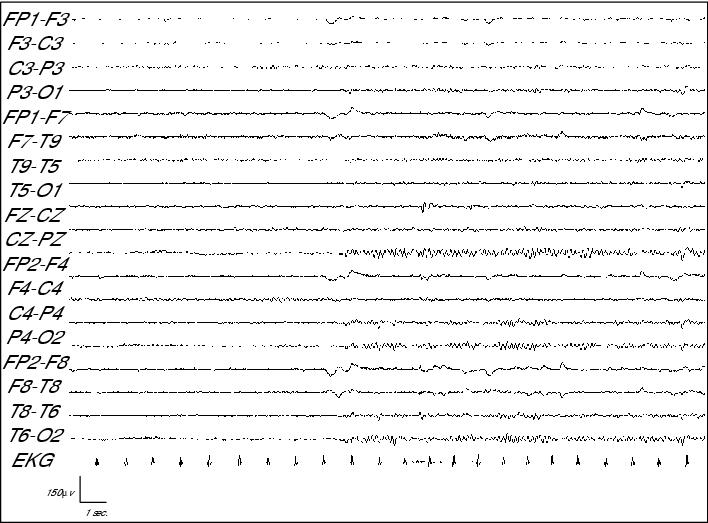
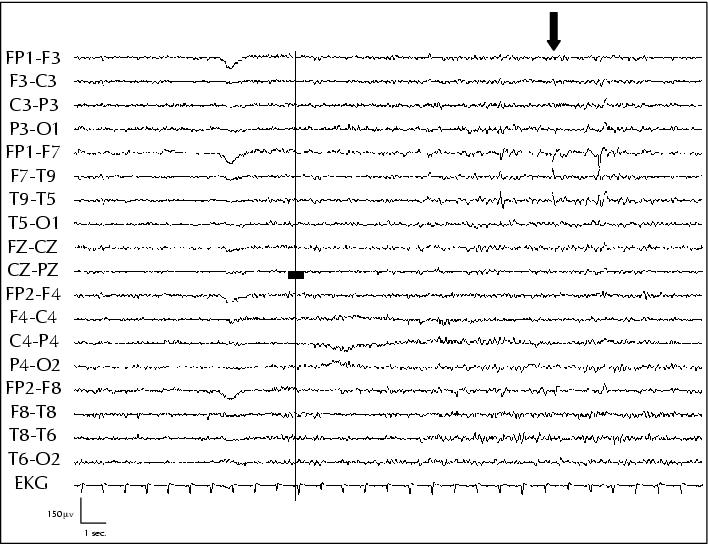
Figure 11. Interictal EEG of patient 6 showing left temporal spikes.
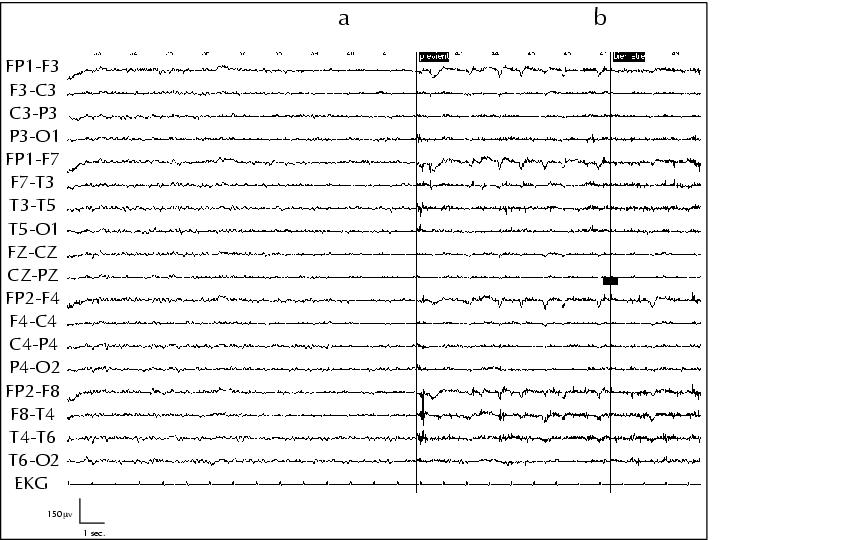
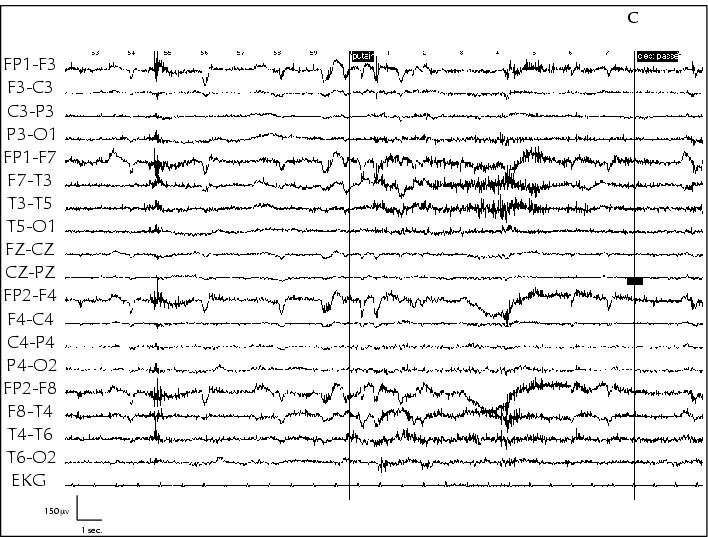
Figure 12. Ictal EEG of a âpleasant feelingâ seizure in patient 6. The only abnormality observed is that of a flattening of brackground EEG activity at seizure onset (a, b pleasant feeling; c end of seizure).

