Epileptic Disorders
MENUCognitive outcomes of different surgical approaches in temporal lobe epilepsy Volume 15, issue 3, September 2013
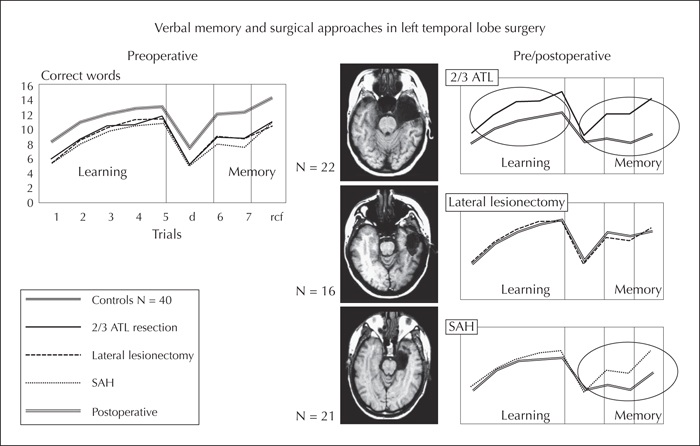
Figure 1 Pre- and postoperative verbal learning and memory (VLMT /German AVLT) in left TLE patients with hippocampal pathology who underwent ATL versus SAH and patients with lateral lesions who underwent cortical lesionectomy. Before surgery, the three groups showed similar impaired memory (left panel). Excellent outcome was observed after lesionectomy, a decrease in long-term retrieval after ATL and SAH, and a decrease in learning after ATL.
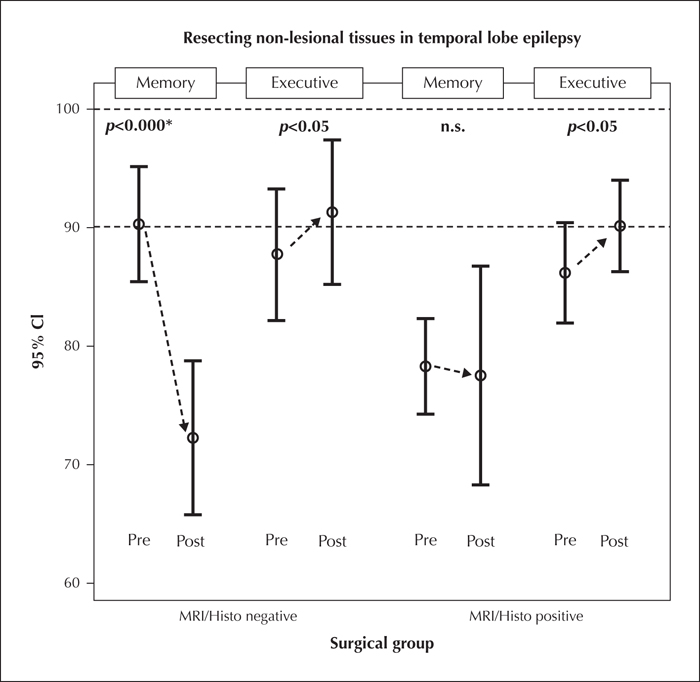
Figure 2 Differential pre- and postoperative combined memory (verbal/nonverbal: VLMT German AVLT, DCS-R) and executive score (letter cancellation/verbal fluency) for 10 left- and 5 right-sided resected patients with MRI and histopathologically-negative TLE versus 15 matched lesional controls. Note the group difference in memory disfavouring lesional patients at baseline, the highly significant drop in memory in non-lesional patients, and the similar memory performance in both groups after surgery. Non-memory functions tended to improve in both groups, which may by part be due to a practice effect.
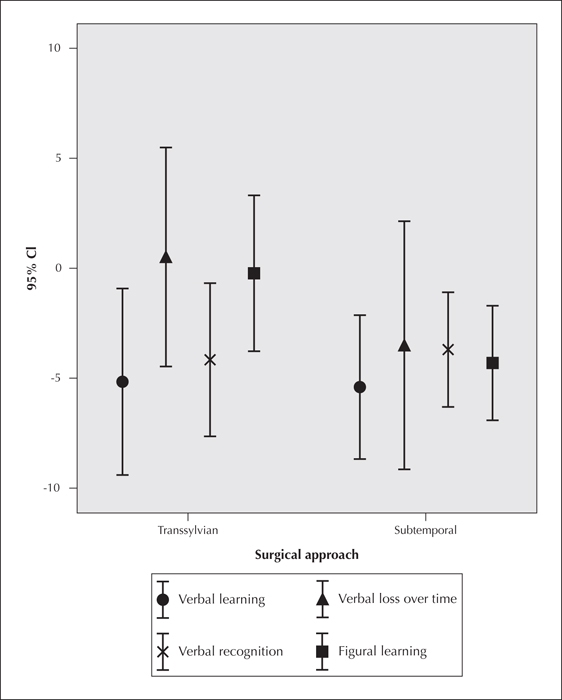
Figure 3 Verbal (VLMT: German AVLT) and figural memory (DCS-R) outcome as a function of surgical approach (trans-sylvian versus subtemporal). Difference in scores (postoperative minus preoperative; standard values: one SD=10; negative values are losses and positive values gains) for verbal learning, memory (loss), and recognition and for figural learning are presented, independent of the side of surgery. The comparable negative effects of surgical approaches on verbal learning and the differential effect on figural learning, which deteriorated particularly after subtemporal surgery, is noted.
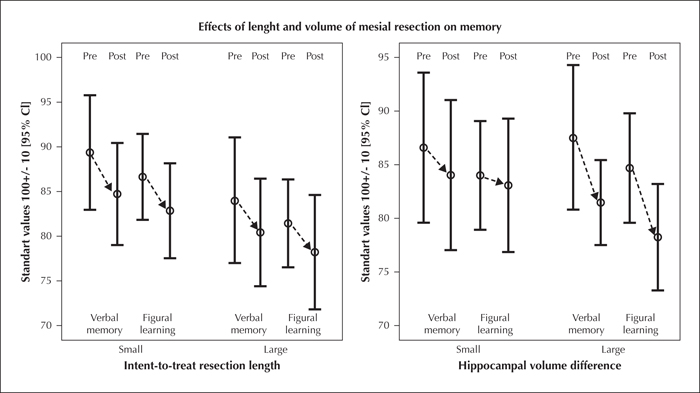
Figure 4 Verbal (VLMT: German AVLT) and figural memory (DCS-R) outcome in patients with left M-TLE after SAH as a function of the intended hippocampal resection length (2.5 versus 3.5 cm) and the resected hippocampal volume (median split). Scores represent standard scores with mean=100, SD=10. The resected volume, taking preoperative pathology into account but not the intended resection length, is related to verbal and figural memory outcome.
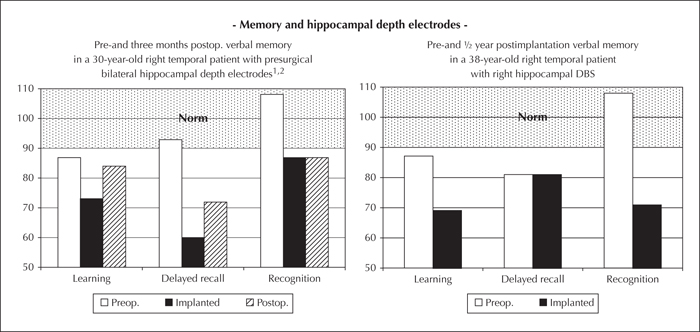
Figure 5 Left panel: impact of bilateral hippocampal depth electrodes and right SAH on verbal learning, memory, and recognition (VLMT: German AVLT: standardised values 100±10) in a patient with right M-TLE. Right panel: effect of chronic depth electrode implantation and stimulation on verbal learning, memory, and recognition (standardised values 100±10) in a patient with right M-TLE.

