Annales de Biologie Clinique
MENULupus anticoagulant and ischemic strokes: about two case reports Volume 79, issue 4, Juillet-Août 2021
Authors
1 Service d’hématologie biologique, CRMR des MAT-laboratoire ADAMTS13, CRMR de la Maladie de Willebrand, Hôpital Lariboisière, AP-HP Nord, Université de Paris, Paris, France
2 Inserm UMR-S 1140 Innovations thérapeutiques en Hémostase, Faculté de Pharmacie, Université de Paris, Paris, France
3 EA-3518 Recherche clinique en hématologie, immunologie et transplantation, Groupe MicroAngiopathies Thrombotiques, VWF et ADAMTS13, Institut de Recherche Saint Louis - Université de Paris, Paris, France
4 Service de neurologie - Centre de référence des maladies vasculaires rares du cerveau et de l’œil (CERVCO), Hôpital Lariboisière, AP-HP Nord, Université de Paris, Paris, France
* Correspondance
- Key words: antiphospholipid syndrome, ischemic stroke, antiphosholipid antibodies, lupus anticoagulant
- DOI : 10.1684/abc.2021.1662
- Page(s) : 361-7
- Published in: 2021
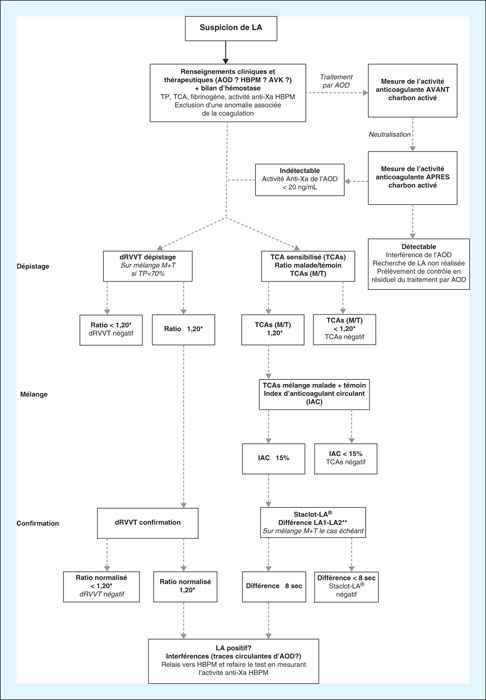
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune disease characterized by thrombotic clinical manifestations, including ischemic stroke. Testing for lupus anticoagulant (LA) among antiphospholipid antibodies is key to the diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). Given the impact on patient management, close clinician-pathologist collaboration is crucial for the presence of LA in a thrombotic setting. Testing for LA must be carried out using specific and appropriate clotting assays and the pathologist should be aware of interferences. We report here two cases of stroke associated with the presence of LA, and recall the strategy for screening for LA.