Epileptic Disorders
MENUHippocampal deep brain stimulation: a therapeutic option in patients with extensive bilateral periventricular nodular heterotopia: a case report Volume 22, numéro 5, October 2020
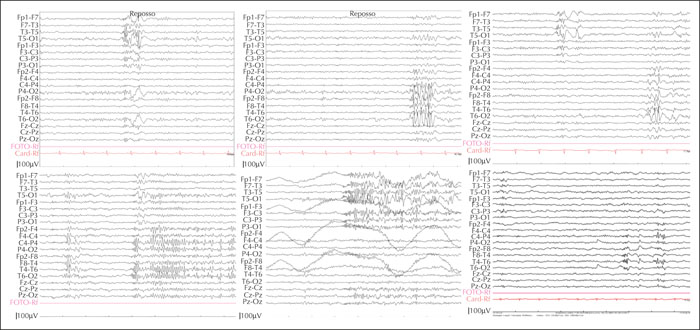
Figure 1
Upper panels: interictal activity prevailing over the left temporal lobe (left), over the right temporal lobe (middle) or seen bilaterally (right). Lower panels: a short electrographic seizure prevailing over the posterior right temporal lobe (left), a short electrographic seizure prevailing over the mid-posterior left temporal lobe (middle), and post-operative (two years) recording showing much less frequent spiking over both temporal lobes independently (right).
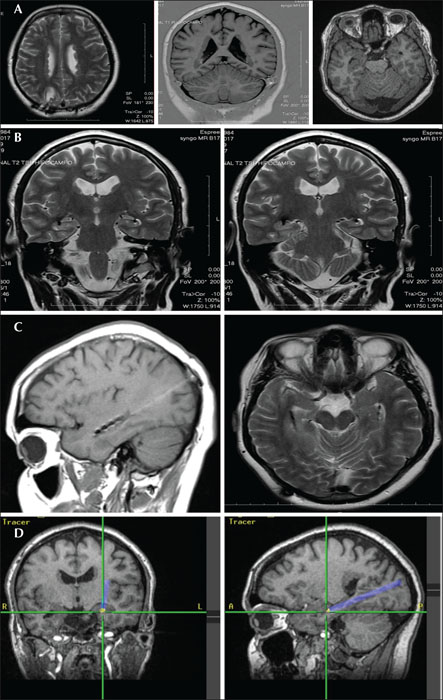
Figure 2
MRI investigation. (A) Extensive bilateral periventricular nodular heterotopia. (B) The location of DBS electrodes bilaterally; contacts are located in the lateral hippocampus proper (left hippocampus) or in the heterotopia/hippocampus interface (right mesial region). (C) Axial and sagittal MRI slices showing the position of the contacts postoperatively. (D) Intraoperative neuronavigational snapshot during electrode insertion.

