Epileptic Disorders
MENUSeizure semiology: ILAE glossary of terms and their significance Volume 24, numéro 3, June 2022
A young child with a generalized seizure, starting with a bilateral muscle jerk in the shoulders (myoclonic), followed by muscle activity cessation (atonia), resulting in a fall.
> Download
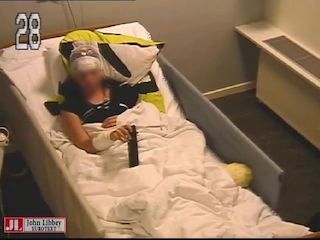 The patient is sitting in bed and watching TV. The seizure starts abruptly with fearful behavior, followed by integrated automatisms. During the seizure, there is impaired awareness. After the seizure ends, the patient answers the nurse’s questions and follows commands.
The patient is sitting in bed and watching TV. The seizure starts abruptly with fearful behavior, followed by integrated automatisms. During the seizure, there is impaired awareness. After the seizure ends, the patient answers the nurse’s questions and follows commands.
 An infant with a myoclonic seizure showing a sudden, very brief bilateral muscle jerk of the upper limbs. The second movement is a reactive movement, as the spontaneous seizure jerk scares the child.
An infant with a myoclonic seizure showing a sudden, very brief bilateral muscle jerk of the upper limbs. The second movement is a reactive movement, as the spontaneous seizure jerk scares the child.
 A patient with a bilateral synchronous clonic seizure.
A patient with a bilateral synchronous clonic seizure.
 A focal seizure with impaired awareness arising from the frontal lobe during sleep. Note that the patient is sleeping on a mattress on the floor with protective mattresses around him. The seizure starts with fulminant hyperkinetic behavior, followed by a gyratory movement of the body to the right. The patient’s awareness is impaired and he is not responding to the nurse’s commands. In the immediate postictal phase, the patient becomes responsive, and is able to point to the window, in response to the verbal command.
A focal seizure with impaired awareness arising from the frontal lobe during sleep. Note that the patient is sleeping on a mattress on the floor with protective mattresses around him. The seizure starts with fulminant hyperkinetic behavior, followed by a gyratory movement of the body to the right. The patient’s awareness is impaired and he is not responding to the nurse’s commands. In the immediate postictal phase, the patient becomes responsive, and is able to point to the window, in response to the verbal command.
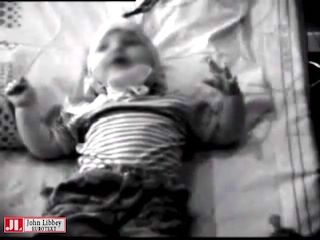 An infant with clusters of epileptic spasms. Note the typical gestalt of the spasms with flexion in the neck and simultaneous abduction in the shoulders and flexion in the hips.
An infant with clusters of epileptic spasms. Note the typical gestalt of the spasms with flexion in the neck and simultaneous abduction in the shoulders and flexion in the hips.
 Generalized tonic-clonic seizure occurring during sleep. The patient lies in the bed in prone position. The seizure starts with ictal crying -the characteristic sound produced by the forced push of air through the airways, due to the tonic contraction of the diaphragm. Symmetric tonic contraction of all four limbs is then observed, followed by symmetric clonic jerks which gradually decrease in frequency.
Generalized tonic-clonic seizure occurring during sleep. The patient lies in the bed in prone position. The seizure starts with ictal crying -the characteristic sound produced by the forced push of air through the airways, due to the tonic contraction of the diaphragm. Symmetric tonic contraction of all four limbs is then observed, followed by symmetric clonic jerks which gradually decrease in frequency.
 A focal impaired awareness seizure that starts with gestural automatisms and continues with ictal aphasia. The patient does not follow verbal commands, but follows visual clues.
A focal impaired awareness seizure that starts with gestural automatisms and continues with ictal aphasia. The patient does not follow verbal commands, but follows visual clues.
 A patient with an atonic seizure, presenting as atonia of the neck and trunk musculature
A patient with an atonic seizure, presenting as atonia of the neck and trunk musculature

