Epileptic Disorders
MENUEvaluation of absences and myoclonic seizures in adults with genetic (idiopathic) generalized epilepsy: a comparison between self-evaluation and objective evaluation based on home video-EEG telemetry Volume 23, numéro 5, October 2021
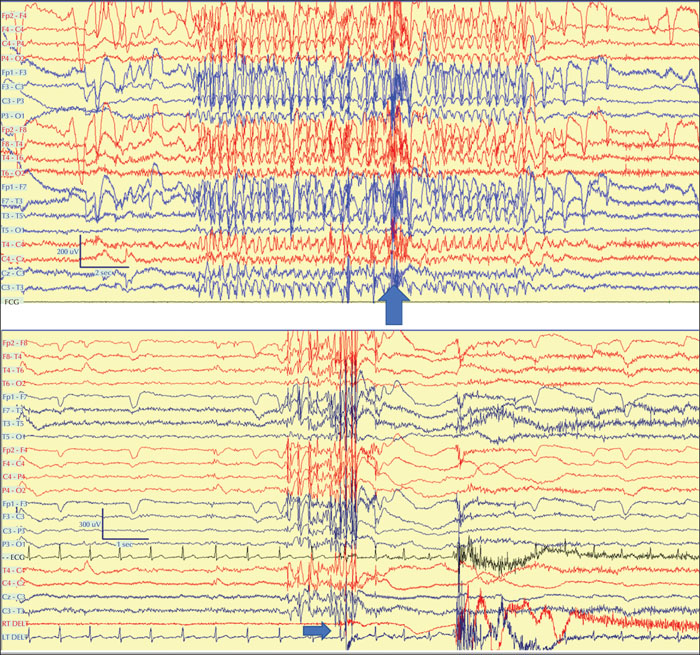
Figure 1
Upper trace: unreported absence in Patient 7. The vertical arrow marks the time of the ictal oral automatisms (for other clinical manifestations, see case vignette in text). Lower trace: typical MS in Patient 11 (see relevant case vignette in text). The seizure occurred as she was on the phone and the associated myoclonic jerk was clearly visible on video. The horizontal arrow shows the EMG potential from both deltoids. This patient missed all her MS.

Figure 2
Brief 3-Hz GSWD during the 66-hour long HVET in Patient 2. Despite its brevity, the discharge is associated with her habitual unpleasant feeling of “light headedness”, and is therefore identified by the patient. Note the ictal blinking and that three seconds later, she reaches for the sheet to document the event (arrow). She also pressed the event button a few seconds later (not shown here). Gain: 10μV/mm; LFF: 0.53Hz; HFF: 70Hz.
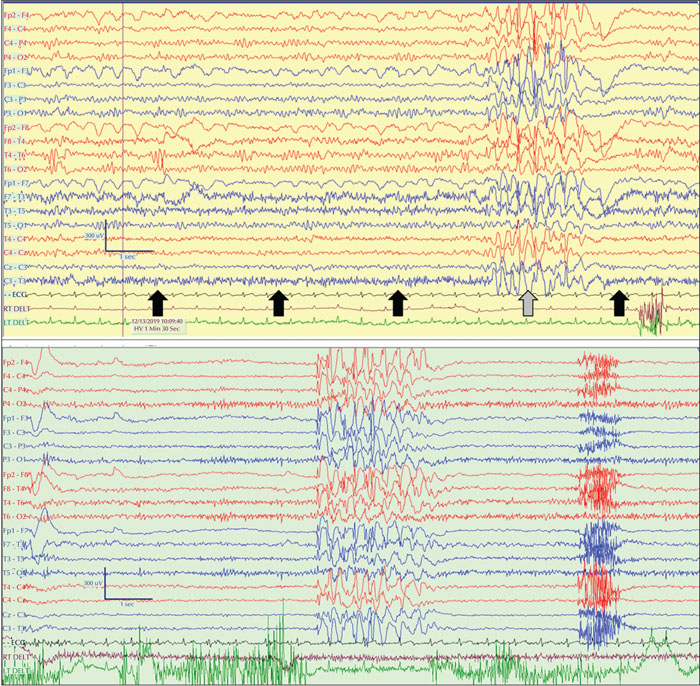
Figure 3
Upper trace: a 2.5-second TA in Patient 8 was recorded during hyperventilation with breath counting on baseline video-EEG, just before the ambulatory part of the HVET. The regular rate of her sequential breathing, shown by the first three black arrows, is apparently distorted by the GSWD. The grey arrow shows the time her next breath was expected and the black arrow on the right, the time it actually occurred. The patient felt this delay as she smiled shortly afterwards. Lower trace: a longer discharge during the HVET, associated with a similar motor arrest (note the pause of EMG activity from the deltoids). The patient was not in view of the camera on this occasion.
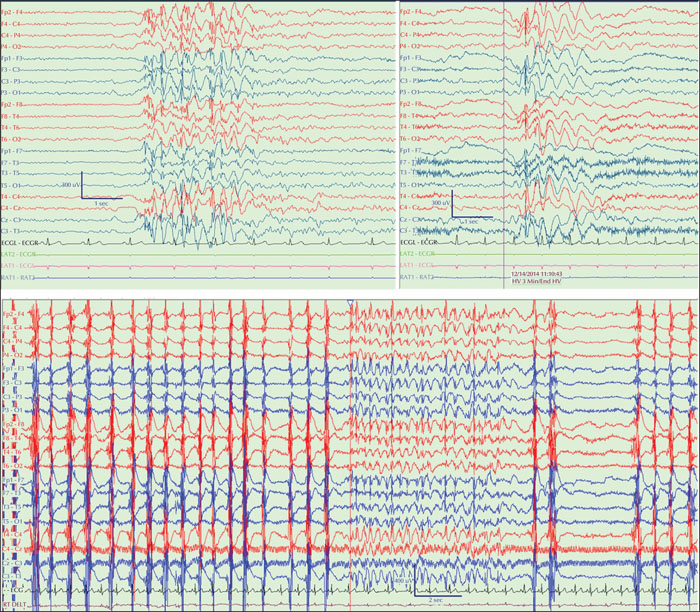
Figure 4
Upper trace: subclinical GSWD in sleep (left) and during hyperventilation with breath counting on awakening on baseline video-EEG, just before the HVET, in Patient 9. Previous video EEGs had recorded TAs >4-5 seconds. Lower trace: motor arrest over the duration of a long GSWD, lasting >6 seconds, during the ambulatory part. Similar motor arrests occurred with other GSWDs.

