Epileptic Disorders
MENUNon-ketotic hyperglycaemia presenting as epilepsia partialis continua Volume 18, numéro 2, June 2016
Illustrations
- Mots-clés : epilepsia partialis continua, non-ketotic hyperglycemia, brain magnetic resonance imaging
- DOI : 10.1684/epd.2016.0833
- Page(s) : 201-3
- Année de parution : 2016
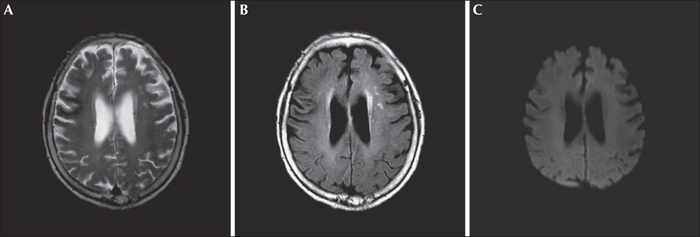
Epilepsia partialis continua is a rare epileptic syndrome observed in patients with brain structural lesions and metabolic disorders. We report a patient with non-ketotic hyperglycaemia presenting as epilepsia partialis continua with reversible focal brain lesions. An 83-year-old woman visited our hospital due to sudden and repetitive left facial twitching lasting for two days. Initial laboratory data revealed serum glucose, osmolality, and sodium levels of 631 mg/dl, 310 mOsm/l, and 130 mEq/l, respectively. EEG was normal. Brain MRI showed low signal changes in the right frontal subcortical area and high signal changes in the surrounding right frontal cortical areas on T2-weighted, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery, and diffusion-weighted images. No seizures recurred after correcting blood glucose levels, hydrating the patient, and infusing valproate (900 mg/day). Follow-up MRI, six months later, showed complete resolution of the signal changes in the right frontal cortical and subcortical areas and no clinical seizures. When considering non-ketotic hyperglycaemia with epilepsia partialis continua in an elderly patient, early diagnosis and administration of the appropriate therapy is very important in order to decrease morbidity.