European Journal of Dermatology
MENUIntravenous immunoglobulin-induced thrombocytopenia: a case report and review of the literature Volume 32, numéro 3, May-June 2022
- Mots-clés : adverse event, intravenous immunoglobulin, thrombocytopenia
- DOI : 10.1684/ejd.2022.4271
- Page(s) : 373-6
- Année de parution : 2022
Background
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), a pooled blood product acquired from multiple healthy donors, is an effective treatment for various types of autoimmune diseases, haematological disorders, and infectious diseases. Adverse haematological events such as throm-bocytopenia are rarely caused by IVIG.
Objectives
To investigate the phenomenon of IVIG-induced thrombocytopenia.
Materials & Methods
A case study and a review of the previous literature based on a search using MEDLINE (PubMed) and ICHUSHI (for Japanese literature) electronic databases.
Results
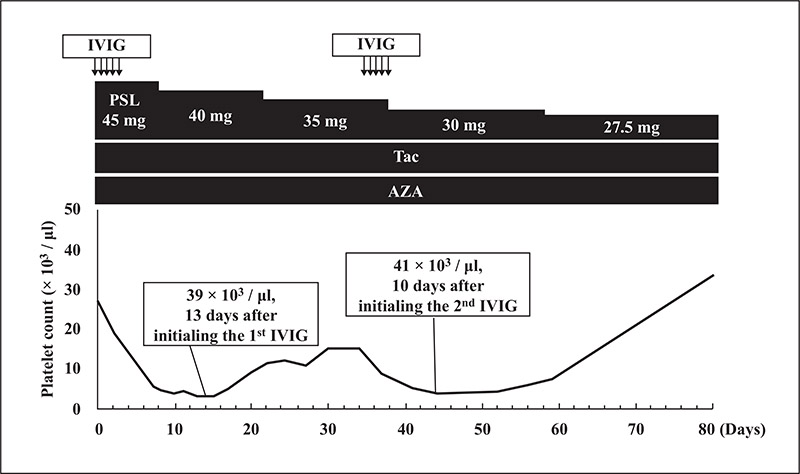
The present case of dermatomyositis exhibited two episodes of IVIG-induced thrombocytopenia, which occurred a few days after initiating IVIG and was significant within two weeks without haemorrhagic symptoms. Spontaneous remission of thrombocytopenia was repeatedly observed. Based on a review of five cases, the underlying disorders were autoimmune bullous diseases in three of the five cases. Polyethylene glycol-treated human immunoglobulin products were used in three of the five cases. The clinical course of IVIG-induced thrombocytopenia was similar to that in our present case.
Conclusion
Because of the rarity of severe haemorrhagic symptoms and spontaneous remission of IVIG-induced thrombocytopenia, discontinuation of IVIG due to thrombocytopenia is not straightforward.