Epileptic Disorders
MENUSomatosensory reflex epilepsy: simultaneous video-EEG monitoring and surface EMG Volume 20, numéro 1, February 2018
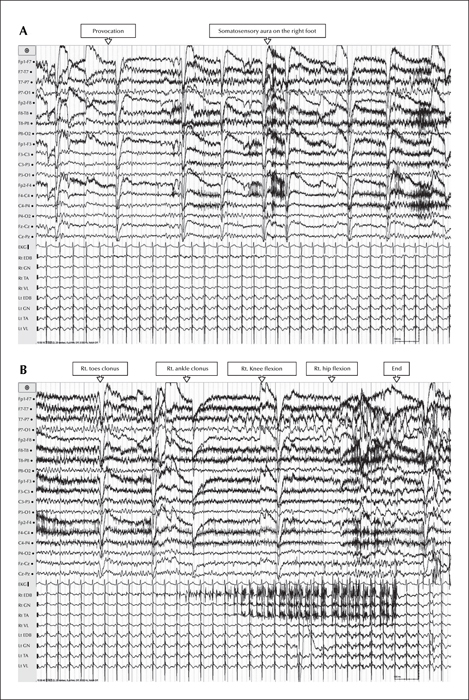
Figure 1
EEG (upper panel) and sEMG (lower panel) on both lower extremities during a typical attack ([B] is a continuation of [A]). The EEG shows rhythmic theta activity on the posterior temporal area; the EMG shows sequential progression of involved muscles, from the extensor digitorum brevis, across the gastronecmius and tibialis anterior, to the vastus lateralis. EDB: extensor digitorum brevis; GN: gastronecmius; TA: tibialis anterior; VL: vastus lateralis; Rt: right; Lt: left.

