Epileptic Disorders
MENUQuantitative MR and cognitive impairment in cryptogenic localisation-related epilepsy Volume 16, numéro 3, September 2014
- Mots-clés : cognition, diffusion tensor imaging, localization-related epilepsy, memory, MR spectroscopy, MRI-negative
- DOI : 10.1684/epd.2014.0665
- Page(s) : 318-27
- Année de parution : 2014
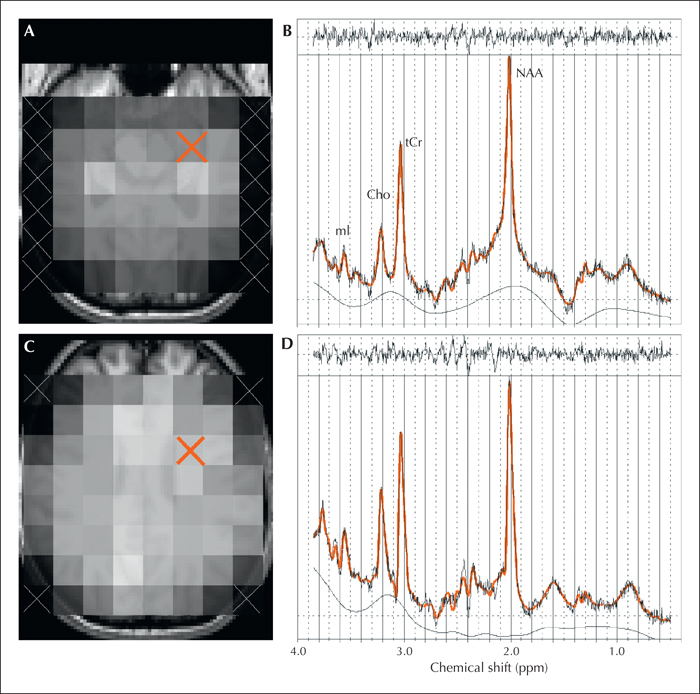
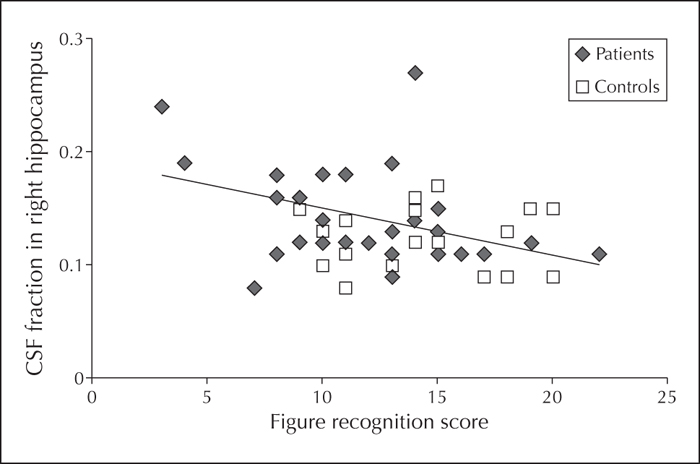
For patients with chronic cryptogenic localisation-related epilepsy (CLRE), conventional MRI does not provide measures to discern between patients with or without cognitive complaints. We investigated, in a preliminary study, whether it is possible to detect cerebral biomarkers of cognitive impairment in patients with CLRE using sensitive quantitative MRI techniques. Neuropsychological assessment and quantitative 3.0 T MRI, comprising T2 relaxometry, diffusion tensor imaging, and spectroscopic imaging, were applied to 35 patients with CLRE and 21 healthy controls. Analysis included the left and right hippocampi, and frontal and temporal lobes. Differences between the groups and correlations with cognitive and clinical characteristics were assessed. Patients with epilepsy scored significantly worse on cognitive tasks compared to healthy controls. Significantly larger CSF fractions in the hippocampi and left temporal lobe, a longer T2 relaxation time in the left hippocampus, and a significantly higher concentration of glutamate/glutamine in the left frontal lobe were observed in patients with epilepsy. Moreover, poor memory performance was significantly correlated with larger CSF fractions in the right hippocampus and left temporal lobe in patients. In the temporal lobe, an association between subtle changes in morphology (indicative of atrophy) and memory performance was found, consistent with previous literature. These results may help to explain the alterations in brain functioning in patients with epilepsy.